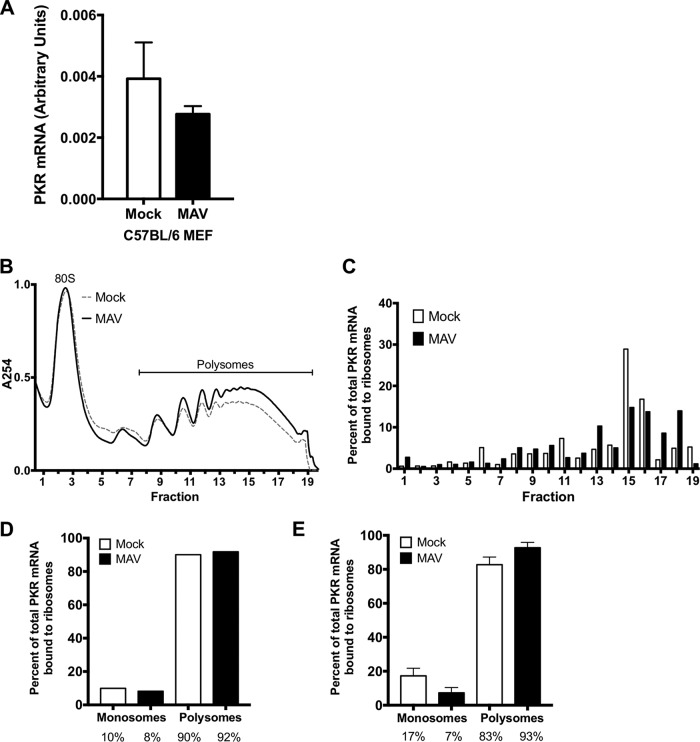
FIG 4.
MAV-1 infection does not affect PKR translation. (A) C57BL/6 MEFs were infected with MAV-1 (MAV) at an MOI of 5 or were mock infected (mock) and collected at 48 hpi. Cells were lysed, and cleared lysates from three 10-cm-diameter plates were layered onto 25% sucrose and centrifuged to pellet ribosomes. RNA was purified from the pellets, cDNA was generated from the RNA, and qPCR was used to quantitate the PKR mRNA levels. The graph represents 9 replicates for each time point, pooled from 3 independent experiments. Error bars show the SEM. (B) C57BL/6 MEFs were infected with MAV-1 (MAV) at an MOI of 2 or were mock infected (mock). Cells were collected at 25 hpi and lysed; cleared lysates were layered onto 10%-to-50% sucrose gradients and centrifuged. Gradients were collected from the top and pumped through a UV spectrophotometer, and 34 fractions were collected. The gradients are displayed with the bottom fractions indicated to the right. The UV trace of the first 10 fractions (including 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits) is not shown. (C) RNA was purified from each fraction of the gradients represented in panel B. cDNA was generated from the RNA, qPCR was used to quantitate PKR mRNA in each fraction, and the results are displayed as the percentages of total PKR mRNA associated with ribosomes. Panels B and C present results from one experiment representative of 3 independent experiments. (D) Percentage of total PKR mRNA associated with monosomes (fractions 1 to 6) and polysomes (fractions 7 to 19) from the trial represented in panels B and C (pooled for mock-infected and infected samples). The percentages represented by each bar are displayed below each bar. (E) Pooled monosome and polysome data (as described for panel D) from three independent experiments. Error bars show the SEM. The percentages represented by each bar are displayed below each bar. There were no significant differences between the mock-infected samples and the infected samples (A and E).