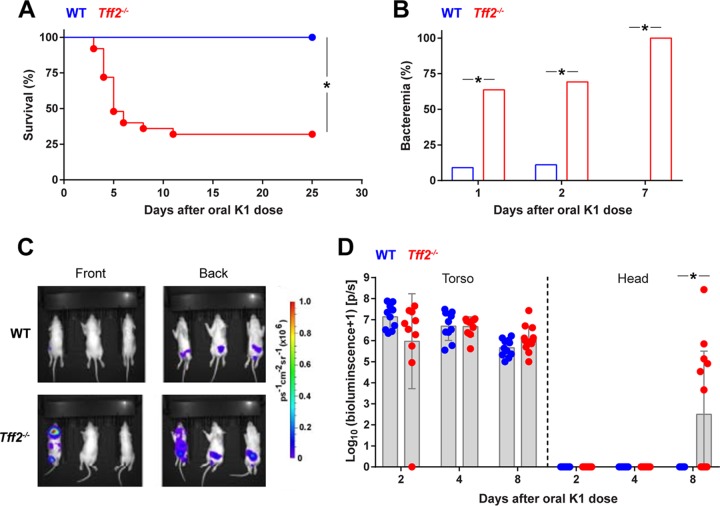
FIG 2.
Tff2-deficient neonatal rat pups exhibit increased susceptibility to E. coli K1 systemic infection. (A) Survival of wild-type and tff2−/− rats dosed orally with 2 × 106 to 6 × 106 CFU E. coli A192PP at P9; n = 13 (wild type) and 25 (tff2−/−). (B) Presence of E. coli K1 bacteria in blood samples from pups dosed with E. coli A192PP at P9 as determined by culture. E. coli K1 colonies were identified using bacteriophage K1E. Day 1, WT, n = 12; day 2, WT, n = 10; day 1, tff2−/−, n = 11; day 2, tff2−/−, n = 13; day 7, WT, n = 12; day 7, tff2−/−, n = 15. χ2 test; *, P < 0.05. (C and D) 2D bioluminescent imaging of pups dosed orally with 2 × 106 to 6 × 106 CFU E. coli A192PP-lux2 at P9. (C) Images showing photoemissions collected from the entire bodies of live animals at day 8 after initiation of colonization (P17). (D) Distribution of bioluminescent bacteria between torso and head. Bioluminescence values were determined as log10 (flux + 1); flux was measured in photons per second (p/s). Shown are means ± standard deviations (SD) (Student’s t test); *, P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test).