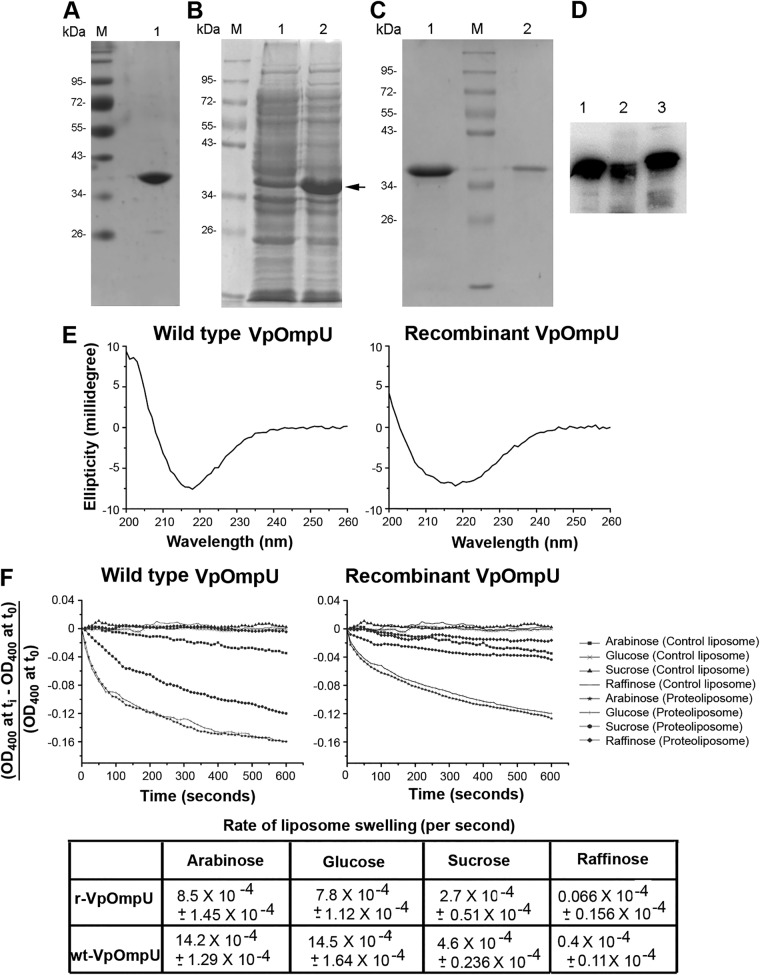
FIG 2.
Characterization of OmpU from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. (A) Lane 1, SDS-PAGE/Coomassie blue staining analysis of the purified form of wt-OmpU extracted from the V. parahaemolyticus outer membrane fraction. Lane M, molecular weight markers. (B) Overexpression of recombinant VpOmpU in E. coli. Protein overexpression was induced with 1 mM IPTG, cells were lysed, and the soluble fraction of the cell lysate (lane 1) and the insoluble inclusion body fraction (lane 2) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The band corresponding to the recombinant VpOmpU is marked. The majority of the VpOmpU protein was found to be associated with the insoluble inclusion body fraction. Lane M, molecular weight markers. (C) Purification of refolded recombinant VpOmpU as analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The recombinant form of VpOmpU was refolded by rapid dilution in a buffer containing 0.5% LDAO (lane 1). Refolded VpOmpU was further purified by size exclusion chromatography on Sephacryl S-200 (lane 2). Lane M, molecular weight markers. (D) Immunoblot analysis of recombinant and wild-type VpOmpU using anti-VpOmpU antiserum. Lane 1, purified form of refolded recombinant His-tagged VpOmpU; lane 2, purified form of refolded recombinant VpOmpU after removal of the N-terminal His tag; lane 3, wt-OmpU extracted from the V. parahaemolyticus outer membrane fraction. (E) Far-UV CD spectra of wild-type and recombinant VpOmpU show negative ellipticity minima at around 218 nm for both proteins. (F) The refolded recombinant form and the wild-type VpOmpU protein show nearly identical trends in the liposome-swelling response. Control liposome, liposome preparation lacking VpOmpU; proteoliposome, liposomes containing VpOmpU. The initial rates of the liposome-swelling response (calculated from the slope of the linear fit of the data over the initial period of 50 s) are shown in the table (r-VpOmpU, recombinant VpOmpU; wt-VpOmpU, wild-type VpOmpU).