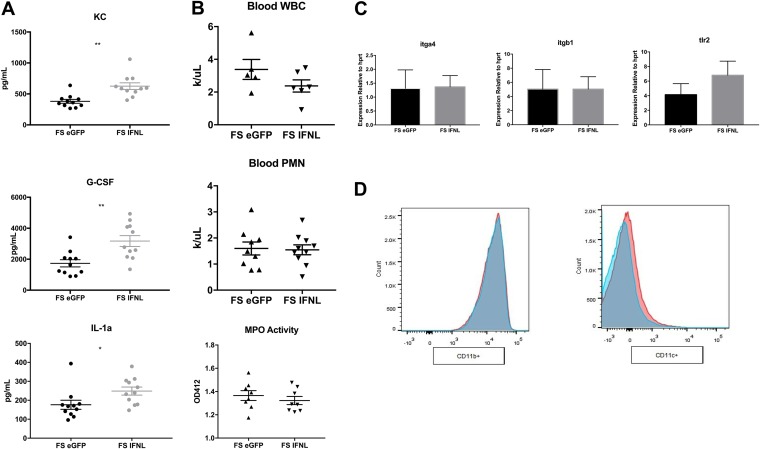
FIG 4.
IFN-λ treatment increases levels of granulocyte chemokines in the lung but does not affect neutrophil production, trafficking, or ROS generation. Mice were infected with influenza, given Ad-IFN-λ or Ad-GFP 5 days later, and challenged with 5 × 107 CFU MRSA 24 h later, as described in the legend of Fig. 1. (A) Cytokine production in lung homogenates (n = 4; three independent experiments). (B) Total white blood cell (WBC) counts and differential counting of blood neutrophils (n = 4; two independent experiments). The left lobe of the lung was perfused with PBS, homogenized, and assayed for myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity as a measure of reactive oxygen species generation (n = 4; three independent experiments). PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocytes. (C) Real-time PCR of the bronchoalveolar lavage cell pellet for neutrophil adhesion molecules and bacterial receptors (n = 4; three independent experiments). (D) Expression of CD11b on live CD45+ Ly6G+ lung neutrophils (n = 4; two independent experiments). Ad-IFN-λ-treated samples are displayed in pink, and Ad-GFP-treated samples are in blue. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.