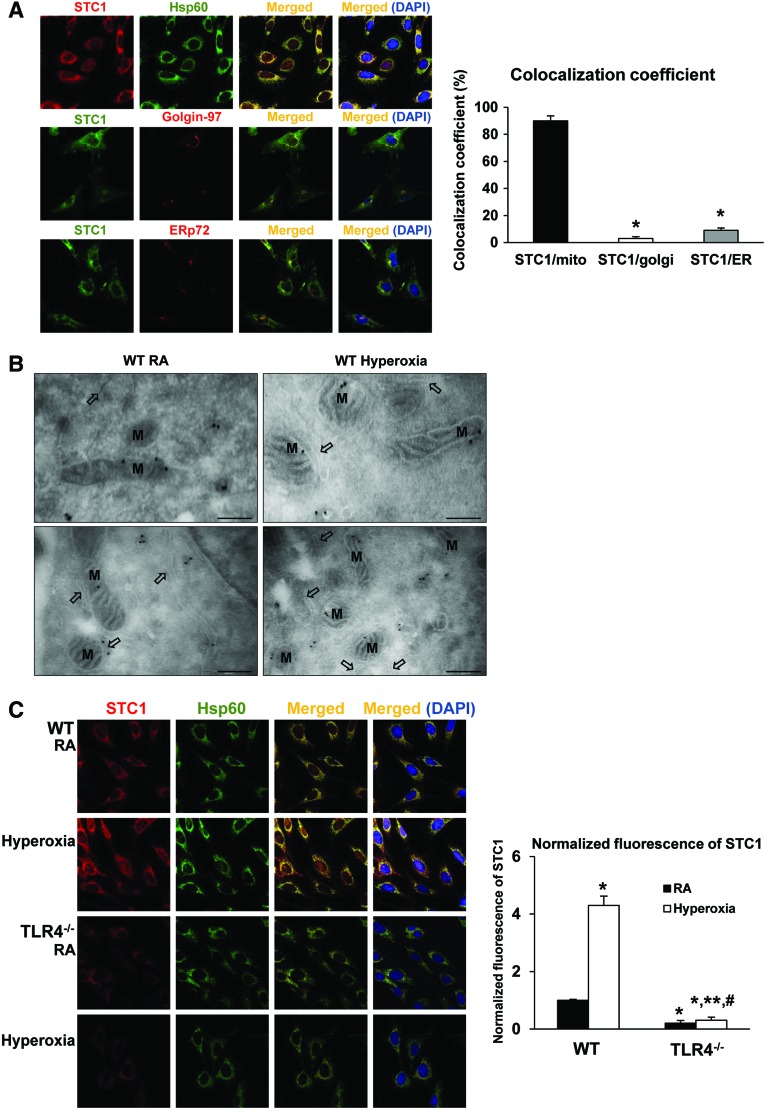
FIG. 6.
TLR4−/− MLECs have decreased mitochondrial STC1 during RA and hyperoxic conditions. (A) Colocalization of STC1 in MLECs. MLECs were immunostained for STC1 plus mitochondrial marker Hsp60, golgi marker Golgin-97, or endoplasmic reticulum marker ERp72. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Left panel shows single immunostained and merged images, original view of all photomicrographs × 1000. Right panel shows the quantification of colocalization; the fraction of STC1 that colocalizes with the cellular organelle markers is represented by the colocalization coefficient. *p < 0.05 vs STC1/mito. Data are representative of at least 20 images. (B) Immunogold labeling of STC1 protein in MLECs. WT MLECs were exposed to 72 h of hyperoxia or RA as control. Note: dense labeling (black deposits) over mitochondria observed with the transmission electron microscopy. M, mitochondria; black arrows, endoplasmic reticulum. Bar = 250 nm. (C) Immunostaining for STC1 (red) and Hsp60 (mitochondria marker, green) with DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) in WT or TLR4−/− MLECs was exposed to 72 h of hyperoxia or RA as control. Left panel shows single immunostained and merged images, original view of all photomicrographs × 1000. Right panel shows the normalized fluorescence of STC1 using the ImageJ software. *p < 0.05 vs WT RA; **p < 0.05 vs WT hyperoxia; #p < 0.05 vs TLR4−/− RA. Data are representative of at least 20 images. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's HSD test calculator for multiple comparisons. Color images are available online.