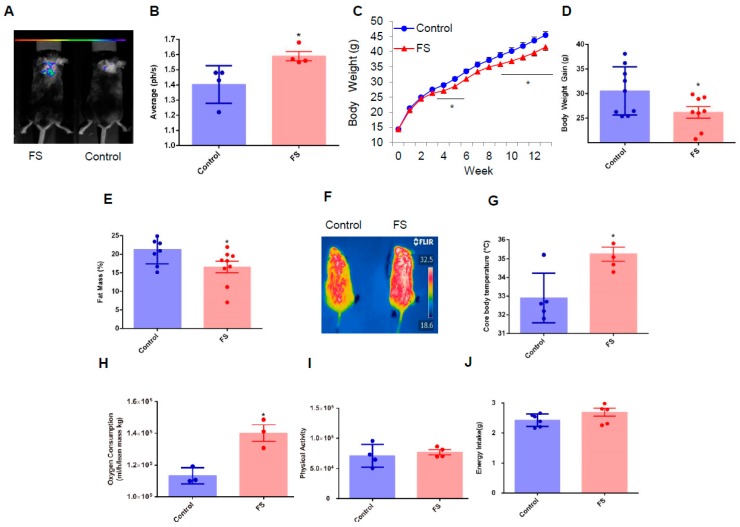
Figure 2.
FS reduces adiposity and increases energy expenditure in HFD mice. (A,B) In vivo imaging of UCP1 transgeneic luciferase male mice treated with saline or FS (1 mg/kg) for one week (n = 4), (C) body weight of C57/BL6 male mice treated by saline (n = 9) or FS (1 mg/kg, n = 8) fed with a high-fat diet from the fourth week, (D) body weight gain of C57/BL6 male mice treated with saline (n = 9) or FS (1 mg/kg, n = 8) in the 14th week, (E) fat mass of HFD male mice treated with saline (n = 8) or FS (1 mg/kg, n = 9) in the 11th week using NMR, (F,G) infrared imaging photos and core body temperature of HFD male mice treated with saline or FS (1 mg/kg) in a cold challenge experiment at 4 °C up to 4 h (n = 5), (H) oxygen consumption bar charts of mice treated with saline or FS in the 14th week for 48 h (n = 3), (I) physical activity of mice treated with saline or FS in the 14th week for 24 h (n = 4), (J) Average energy intake per day of mice treated with saline (n = 12) or FS (n = 10) in the 10th week for six days. Values represent means ± SEM. Error bars represent SEM. Significant differences compared to vehicle controls are indicated by * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 (assessed by Student’s t-test).