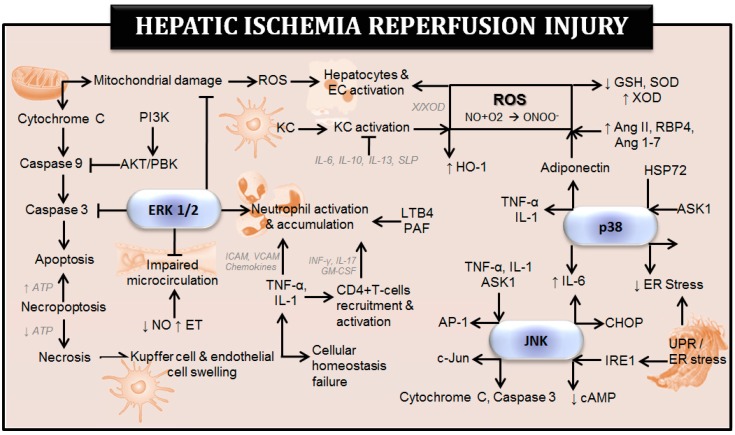
Figure 1.
Effect of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) on the mechanisms involved in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ang: angiotensin; AP-1: activating protein; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; Cyt c: cytochrome c; EC: endothelial cell; ERK 1/2: extracellular signal regulated kinases 1/2; ET: endothelin; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; GSH: glutathione; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; HSP72: heat shock protein 72; ICAM: intracellular cell adhesion molecule; IL: interleukin; JNK: c-jun N-terminal kinase; KC: kupffer cell; LTB4: leucotriene B4; NO: nitric oxide; ONOO-: peroxynitrite; PAF: platelet activating factor; PBK: protein kinase B; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RBP4: retinol binding protein 4; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SLPI: secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor; SOD: superoxide dismutase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; VCAM: vascular cell adhesion molecule; X/XOD: xanthine/xanthine oxidase.