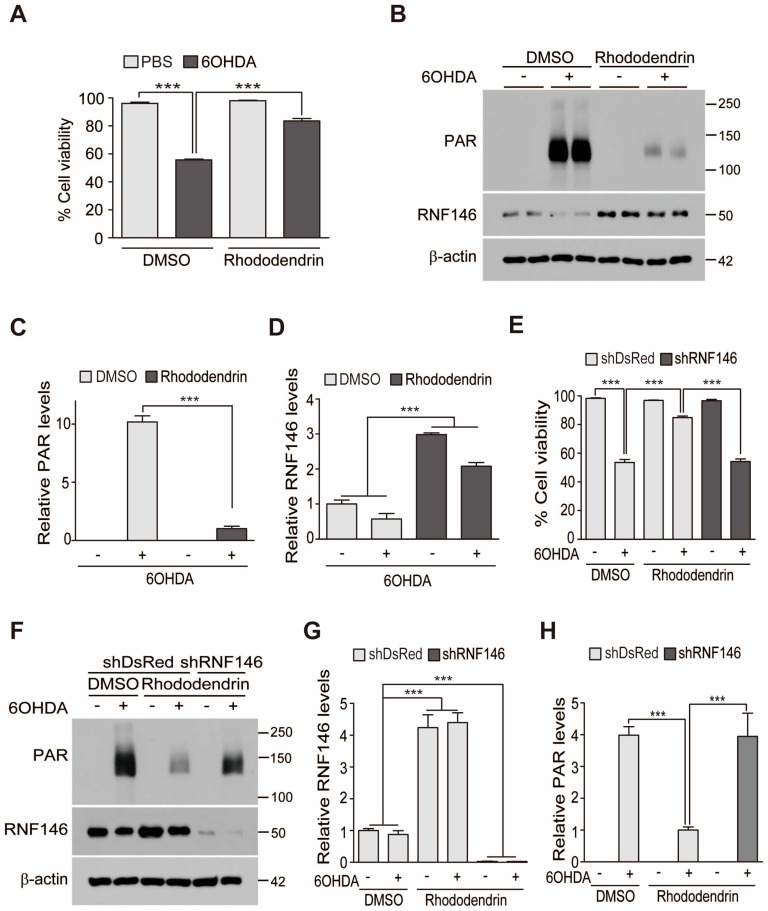
Figure 2.
Rhododendrin-induced RNF146 expression protects SH-SY5Y cells from 6-OHDA toxicity. (A) Trypan blue exclusion cell viability assay demonstrating that rhododendrin pretreatment (10 µM, 37 h) increase cell survival after stimulation with 6-OHDA (70 µM, 16 h) (n = 6). (B) Representative immunoblots showing poly (ADP-ribose) (PAR), and RNF146 expression levels in SH-SY5Y cells challenged with 6-OHDA (70 µM, 30 min) following pretreatment with rhododendrin (10 µM, 37 h) or DMSO vehicle as a control. Quantification of relative PAR (C) and RNF146 (D) expression levels in the experimental groups in panel B. Values are normalized to those of β-actin (n = 3). (E) Trypan blue exclusion cell viability assay demonstrating that rhododendrin protection of SH-SY5Y cells from 6-OHDA (70 µM, 16 h) is RNF146-dependent. Cell survival caused by rhododendrin (10 µM, 37 h) was abolished by transient transfection of shRNA against RNF146 (61 h). shRNA against DsRed (shDsRed) was used as an shRNA transfection control (n = 6). (F) Representative immunoblots showing poly (ADP-ribose) (PAR), and RNF146 expression levels in SH-SY5Y cells transfected (61 h) with the indicated shRNA constructs and subsequently challenged with 6-OHDA (70 µM, 30 min) with or without pretreatment with rhododendrin (10 µM, 37 h) or DMSO vehicle as a control. Quantification of relative RNF146 (G) and PAR-conjugated protein (H) expression levels in the experimental groups in panel F. Values are normalized to those of β-actin (n = 3). Quantified data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA test with Tukey’s post-hoc analysis, *** p < 0.001.