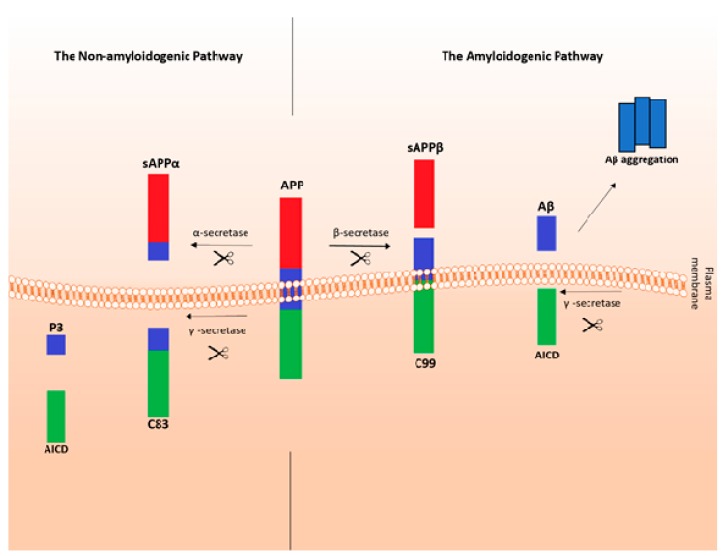
Figure 1.
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing pathways. APP, a transmembrane protein may be processed in two pathways: the amyloidogenic pathway (β-secretase pathway) and the non-amyloidogenic pathway (α-secretase pathway). In the non-amyloidogenic pathway, α-secretase cleaves APP in a way that prevents the formation of amyloid-β (Aβ). It releases the APP C-terminal fragment 83 (C83) and soluble amyloid precursor protein α (sAPPα). C83 is later cleaved by γ-secretase to release the APP intracellular domain (AICD) and P3 fragment. In the amyloidogenic pathway, in turn, β-secretase cleaves APP to release sAPPβ (soluble amyloid precursor protein β), and the APP C-terminal fragment 99 (C99). C99 is later cleaved by γ-secretase, resulting in the release of Aβ and AICD.