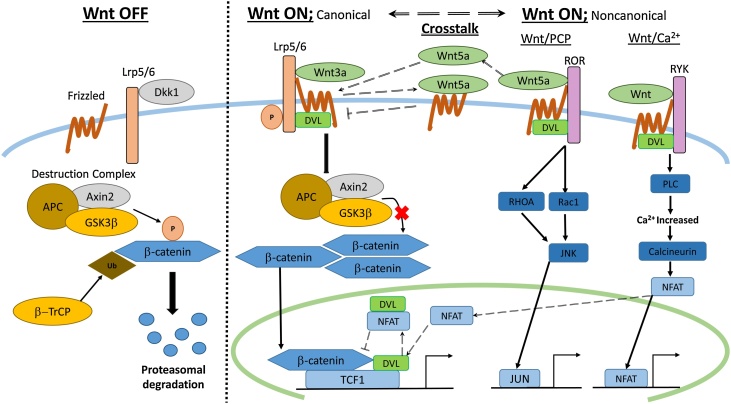
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of Wnt signaling regulation. When the Wnt signaling is off, so-called destruction complex phosphorylate β-catenin followed by βTrCP-induced ubiquitination and its proteasomal degradation. When the Wnt signaling is on, the Wnt/receptor complex initiates downstream signaling via (1) non-phosphorylated β-catenin and transcription factor TCF1 (canonical signaling), (2) JNK (noncanonical Wnt/PCP signaling) or (3) NFAT (noncanonical Wnt/Ca2+ signaling). Both Wnt5a and NFAT can suppress canonical Wnt signaling (dashed arrows). Wnt5a competes with Wnt3a for binding to Frizzled to inhibit the initiation of canonical signaling, while NFAT interacts with nuclear DVL competitively against β-catenin to downregulate downstream gene transcription.