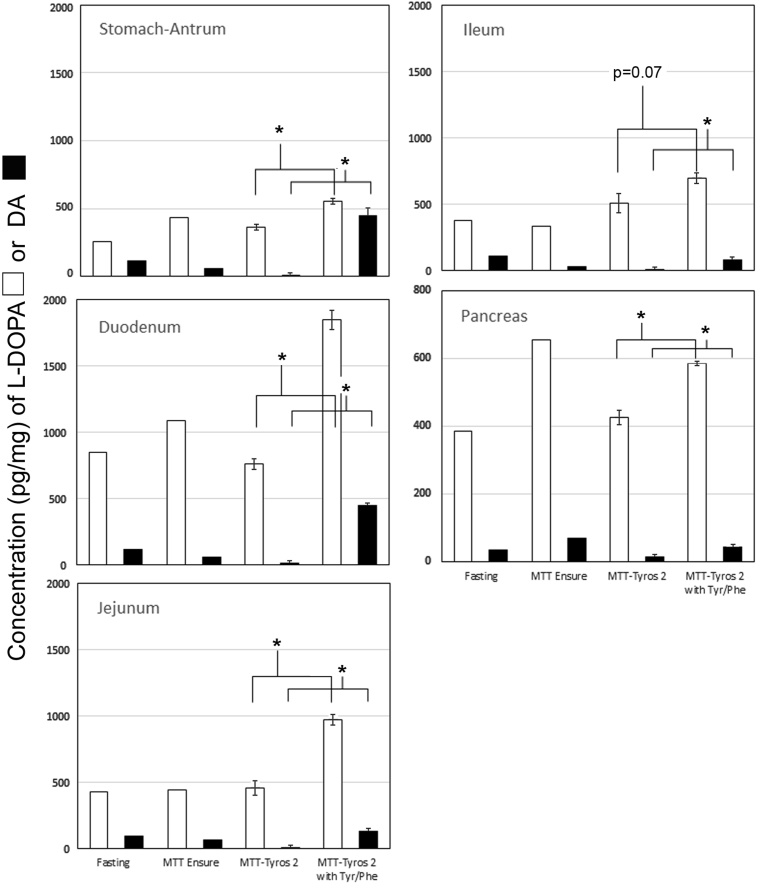
Figure 1.
G.I. tissue L-DOPA and DA content is responsive to the tyrosine and phenylalanine content of the mixed meal stimulus. Male Lewis rats (n = 4 per group) were gavaged with isocaloric mixed meal formulas that differed in tyrosine (TYR) and phenylalanine (PHE) content. Forty-five minutes after gavage, the rodents were euthanized, and tissue from the gut and pancreas was harvested and analyzed for L-DOPA (white bars) and DA (black bars) content using two technical replicates. The mean wet tissue weight normalized monoamine content along the GI tract for each stimulus is displayed. A non-parametric repeated measure ANOVA (Friedman's test) was applied to the data set revealing that GI tissue L DOPA and DA content in Tyros 2 fed animals was significantly lower (p < 0.05) from the three other conditions. Likewise GI tissue L-DOPA-DA content in Tyros 2 + TYR/PHE was significantly higher (p < 0.05) from the three other conditions. The statistical significance of the differences between MMTT-Tyros and MMTT-Tyros + TYR/PHE stimulated L-DOPA and DA tissue content was performed using a two-tailed Students t-test. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Only the statistical significances of the measured differences between Tyros2 and Tyros2 with TYR/PHE are shown (* = p < 0.05).