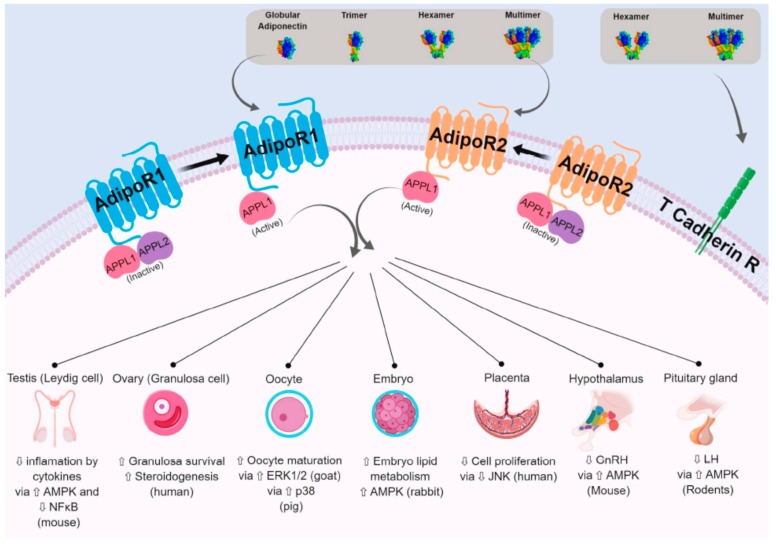
Figure 3.
Adiponectin receptors and some examples of biological effects of adiponectin in reproductive tissues or cells. Adiponectin interacts with adiponectin receptors (mainly AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) to activate or inhibit a number of signalling pathways. T Cadherin receptor (T Cadherin R) binds the hexameric and high molecular weight isoforms of adiponectin but it has no intracellular domain. AdipoR1- and R2-dependent signalling is mediated through APPL 1 and APPL2. In the absence of adiponectin signal, APPL2 can bind to the N-terminal domain of the adiponectin receptors or it can form an APPL1/APPL2 heterodimer which prevents the APPL1/adiponectin receptors binding. On the other hand, the binding of adiponectin to its receptors favours the dissociation of this heterodimer. In peripheral tissues, adiponectin receptors have differing affinities for specific forms of adiponectin. In the reproductive tissues the affinities for specific forms of adiponectin is unknown. However, in these tissues, adiponectin regulates different biological effects through various signalling pathways. ⇧ Increase/stimulation. ⇩ Decrease/inhibition.