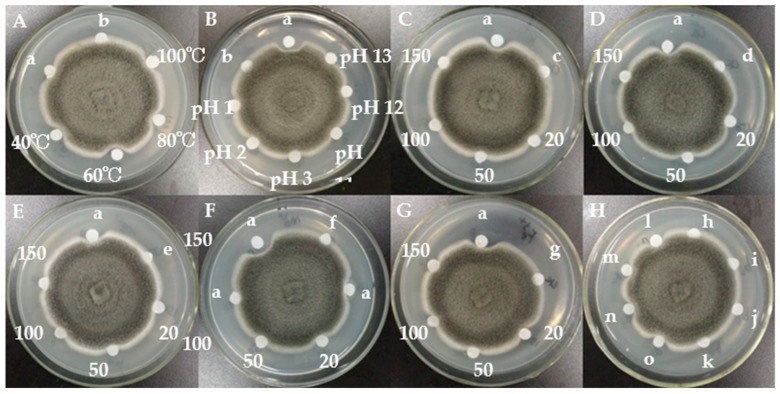
Figure 4.
Effects of heat, acid-base, metal ions, and organic solvents on antifungal activity of BGAP: (A) heat treatment; (B) acid-base treatment; (C) treatment with K+ ions; (D) treatment with Ca2+ ions; (E) treatment with Mg2+ ions; (F) treatment with Mn2+ ions; (G) treatment with Fe3+ ions; (H) organic solvent treatment; a: 20 μL of untreated BGAP solution; b: 20 μL of PBS buffer; c: 20 μL of K+ solution (150 mmol/L); d: 20 μL of Ca2+ solution (150 mmol/L); e: 20 μL of Mg2+ solution (150 mmol/L); f: 20 μL of Mn2+ solution (150 mmol/L); g: 20 μL of Fe3+ solution (150 mmol/L); h: 20 μL of 10% methanol; i: 20 μL of 10% ethanol; j: 20 μL of 10% isopropanol; k: 20 μL of 10% chloroform; 40–100 °C represents 20 μL of BGAP solution treated at the corresponding temperature; pH 1–13 represents 20 μL of BGAP solution treated with the corresponding acid-base; 20–150 represents 20 μL of BGAP solution treated with each metal ion at a concentration of 20–150 mmol/L; l, m, n, o represent BGAP solution treated with 10% methanol, 10% ethanol, 10% isopropanol and 10% chloroform respectively; and the final concentration of BGAP in all treatment groups was 1 mg/mL.