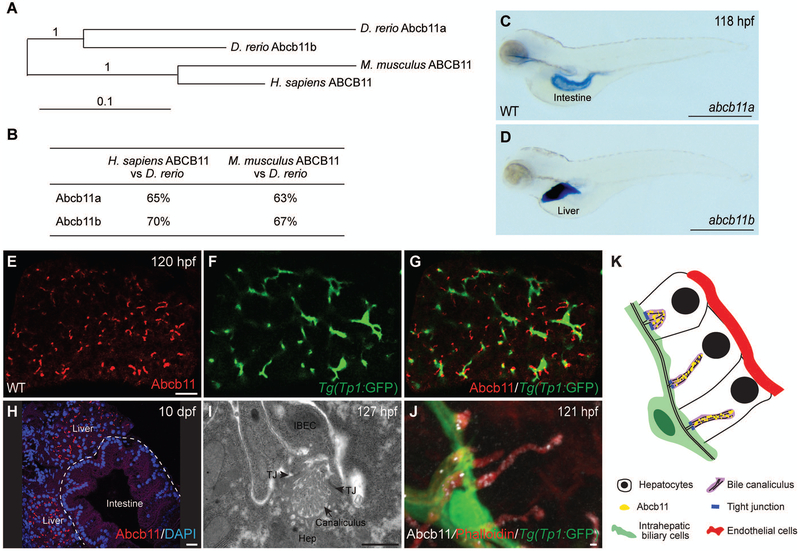
FIG. 1. The zebrafish ortholog of human ABCB11 gene, abcb11b, is expressed in bile canaliculi.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the human, mouse, and zebrafish ABCB11 proteins. (B) ABCB11 protein sequence identity for zebrafish, mouse, and human. (C,D) Expression of the abcb11a and abcb11b transcripts in wild-type (WT) larvae at 118 hours post fertilization (hpf) by whole mount in situ hybridization. Lateral views, anterior to the left. (E-G) Confocal single-plane images showing expression of Abcb11 protein (E) and Tg(EPV.Tp1-Mmu.Hbb:EGFP)/Tg(Tp1:GFP) transgene that labels the intrahepatic biliary cells (F) in WT larva. (G) is a merged image of (E) and (F). Ventral views, anterior to the top. (H) Confocal image showing sagittal section of a WT larva at 10 days post fertilization (dpf): Abcb11 protein (red) is detected in the liver, but not in the intestine (marked by the dashed line). (I) TEM image of a bile canaliculus connecting a hepatocyte (Hep) and an intrahepatic biliary epithelial cell (IBEC) in a WT larva. TJ, tight junction. (J) Confocal three-dimensional projection image showing punctate expression of Abcb11 protein (white) along the bile canaliculi in a WT larva. The canaliculi can be recognized by bright phalloidin staining (red) due to its enrichment of F-actin cytoskeleton. Tg(Tp1:GFP) transgene expression (green) marks the intrahepatic biliary cells. (K) Diagram showing the organization of liver cells in zebrafish. Scale bars: (C,D) 1 mm; (E-H) 20 μm; (I,J) 1 μm.