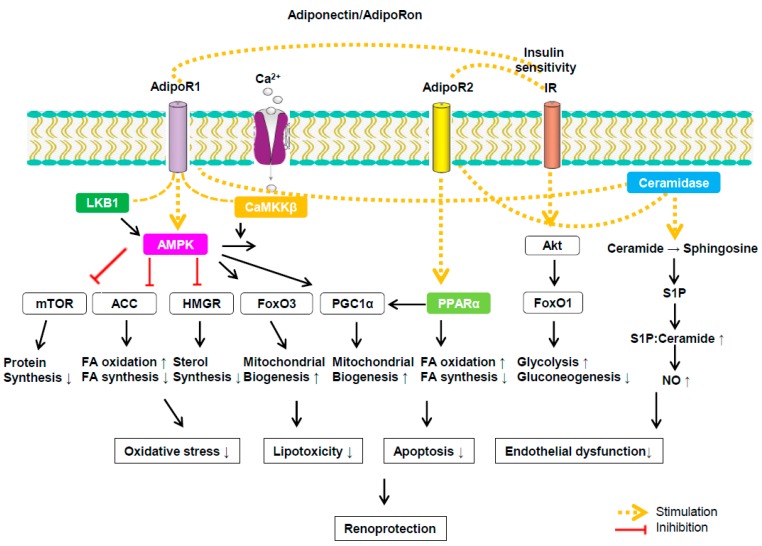
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways associated with adiponectin and its receptor binding. AdipoR1 increases calcium influx to activate Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β (CaMKKβ) and subsequent downstream kinases. AdipoR1 also activates liver kinase B1 (LKB1) and AMPK that can increase peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1) expression. Activation of associated downstream pathways exert prometabolic effects by enhancing fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial biogenesis. AdipoR2 activate PPARα to increase fatty acid oxidation and insulin sensitivity. AdipopR1/2 has ceramidase activity and can catalyze the conversion of ceramide to sphingosine, which produces sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), subsequently increasing S1P to ceramide ratio that further ameliorates endothelial dysfunction through increased NO level. Insulin-stimulated FoxO1 phosphorylation through PI3K and AKT can reduce hepatic gluconeogenesis.