Fig. 3.
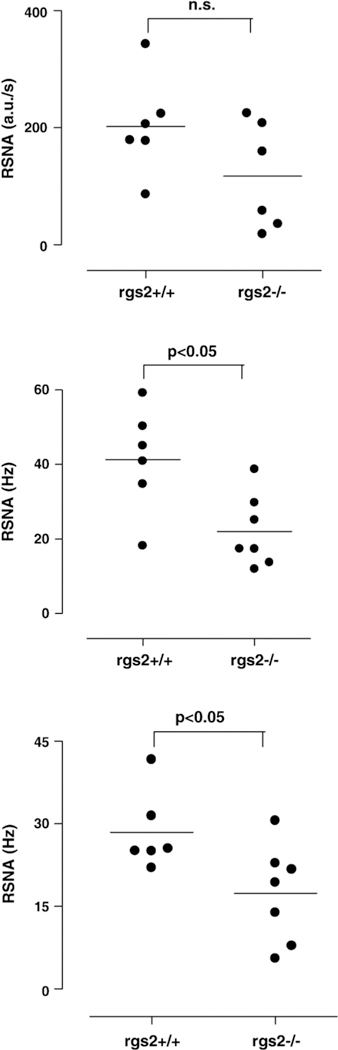
The individual data of renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) for RGS2-deficient (RGS−/−) mice compared to wild-type mice (RGS+/+) determined by three different methods are shown as scatter plots. Top- RSNA calculated as the area under the curve by merely rectifying the nerve signal related to one second in arbitrary units (a.u./s). Middle-the frequency of spikes in Hz calculated using the wavelet de-noising technique. Bottom-classical discriminator method. The frequency of spikes exceeding a preselected threshold voltage was counted per second. Bars represent the mean values. RSNA was lower in RGS2-/- mice compared with RGS2+/+ mice independent of the used method (*p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U-test).
