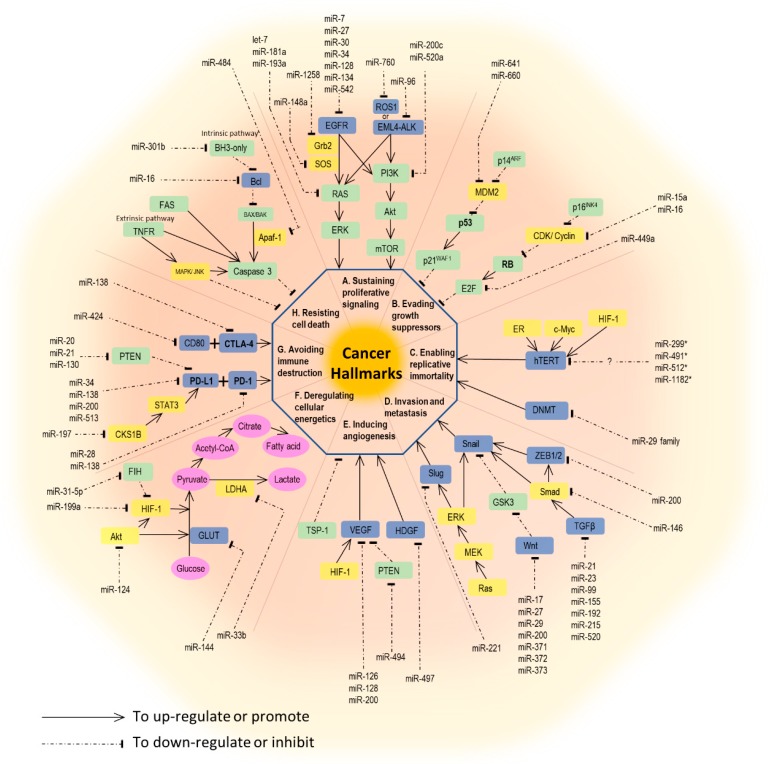
Figure 1.
A diagram of microRNAs and their involved pathways to cancer hallmarks. A. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its receptors, EGFR, conduct proliferative signaling for lung cancer cells through downstream RAS/ERK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. EML4-ALK and ROS1 also initiate cancer cell proliferation through similar pathways. The involved miRNAs are illustrated. B. Deregulations of tumor suppressors, RB and p53, lead the cancer cells evade from growth inhibition. C. The telomerase reverse transcriptase in humans (hTERT) links to the immortality of cancer cells. miR-299, miR-491, miR-512 and miR-1182 are reported to target hTERT. However, these involvements are studied in various cancer cells other than lung cancer. Additionally, miR-29 family can target DNA methyltransferases (DNMT) and control the telomere lengths. D. Snail, Slug, and Wnt are key players involved in epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) with implication of tumor metastasis and invasion. The associated miRNAs are shown in the diagram. E. Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) stand for key participants in promoting tumor angiogenesis. miR-126, miR128 and miR-200 may target VEGF. F. Cancer cells develop aerobic glycolysis as the reprogrammed metabolic pathway. For example, downregulation of miR-144 is found in lung cancer cells with upregulated glucose transporter (GLUT1) expression and increased glucose uptake. G. The interaction of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and its receptor (PD-1) leads the cancer cells evading from immune destruction. miR-34, miR-138, miR-200 and miR-513 target PD-L1 and suppress its expression. H. Fas receptors (intrinsic pathway) and BH3-only proteins (extrinsic pathway) are key participants in the resistance to cell apoptosis. miR-301b targeting BH3-only proteins, and miR-16 targeting Bcl are reported to be involved in cell apoptosis. Note: This diagram is simplified where major, but not all, pathways are illustrated. Meanwhile, cross-talk and interactions between different pathways, not shown in this diagram, might exist. For example, the EGFR signaling pathway might not only promote cell proliferation but also enhance invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and resistance to apoptosis.