Figure 1.
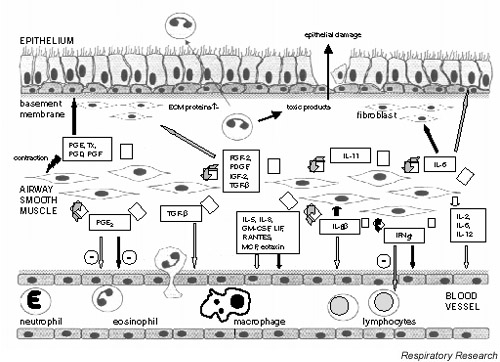
Schematic diagram depicting the role of airway smooth muscle (ASM) cell-derived mediators in airway inflammation. The release of cytokines, chemokines or growth factors (open arrows) can result in ASM as well as inflammatory cell proliferation (dark grey arrows), or the recruitment (light grey arrows) or activation (black arrows) of various cells in the airways. ECM, Extracellular membrane; FGF-2, fibroblast growth factor-2; GM-CSF, granulocyte/macrophage-colony stimulating factor; IGF-2, insulin-like growth factor-2; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; LIF, leukaemia inhibitory factor; MCP, monocyte chemotactic protein; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PG, prostaglandin; RANTES, regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TX, thromboxane.
