Figure 2.
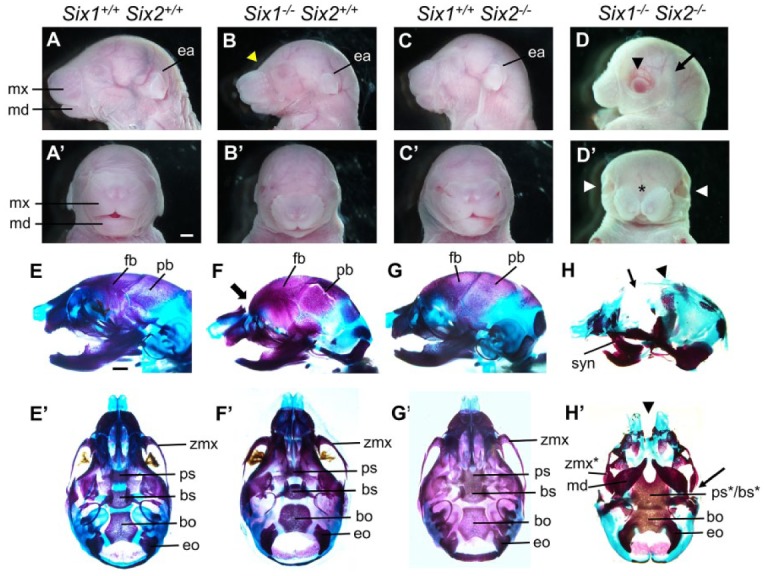
Craniofacial skeletal defects in the Six1 and Six2 compound mutant mice. (A–D′) Lateral view (A–D) and frontal view (A′–D′) of E18.5 heads of the Six1+/+Six2+/+ (A, A′), Six1–/–Six2+/+ (B, B′), Six1+/+Six2–/– (C, C′), and Six1–/–Six2–/– (D, D′) embryos. The yellow arrowhead in B points to the abnormal shape of the forehead. The black arrowhead in D and the white arrowheads in D′ point to widely open eyes. Asterisk in D′ marks midline facial cleft. Scale bar in A’, 1 mm. (E–H′) Lateral view (E–H) and ventral view (E′–H′) of alizarin red– and Alcian blue–stained E18.5 head skeletons of the Six1+/+Six2+/+ (E, E′), Six1–/–Six2+/+ (F, F′), Six1+/+Six2–/– (G, G′), and Six1–/–Six2–/– (H, H′) embryos. The thick arrow in F points to the abnormal shape of the forehead. The thin arrow in H points to lack of frontal bones, and the arrowhead points to the severely reduced parietal bones. The arrowhead in H′ points to the midline facial cleft, and the arrow points to abnormal zygomatic bone. Scale bar in E, 1 mm. bo, basioccipital; bs, basisphenoid; ea, ear; eo, exoccipital; fb, frontal bone; md, mandible; mx, maxilla; pb, parietal bone; ps, presphenoid; syn, syngnathia; zmx, zygomatic process of maxilla. The asterisks in the ps*/bs* and zmx* labels in Panel H point to severe malformation of those structures in the double homozygous mutants.
