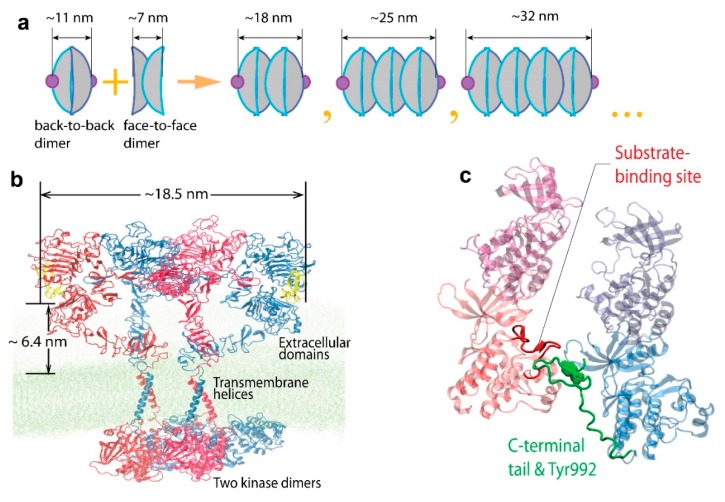
Figure 10.
Model for EGFR oligomerization (figure adapted from Needham et al. (2016) [39]). (a) Illustration of a proposed oligomerization scheme for the EGFR extracellular domain, which depends on repeating back-to-back and face-to-face interactions of the receptor. (b) A complete model of an EGFR tetramer structure, which was formed by the dimerization through the face-to-face interaction of active dimers, showing the predicted separation between the N-termini of the two EGF ligands and the average EGF-membrane distance. (c) The arrangement of the two intracellular active kinase dimers in the tetramer model. The phosphorylation site Tyr992 (green) of one receptor is positioned close to the active site of a kinase domain (red) in the neighboring dimer.