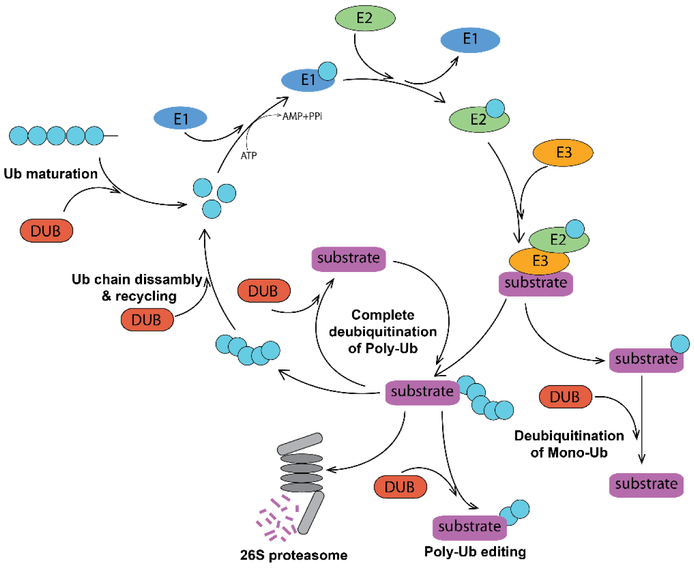
Figure 1. Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and DUBs.
Mono- and polyubiquitination of a protein substrate is catalyzed by consecutive action of E1, E2 and E3 ubiquitinating enzymes. The K48-linked polyubiquitin tag targets the substrate for proteasomal degradation, while monoubiquitination and other ubiquitin linkages result in a different functional outcome. DUBs deubiquitinate both poly- and monoubiquitinated proteins and thus change their fate. DUBs can edit polyubiquitin chains architecture and recycle ubiquitin. They also participate in maturation of the free ubiquitin.
Ub – ubiquitin; E1 – ubiquitin activating enzyme; E2 – ubiquitin conjugating enzyme; E3 – ubiquitin Ligase; DUB – deubiquitinating enzyme.