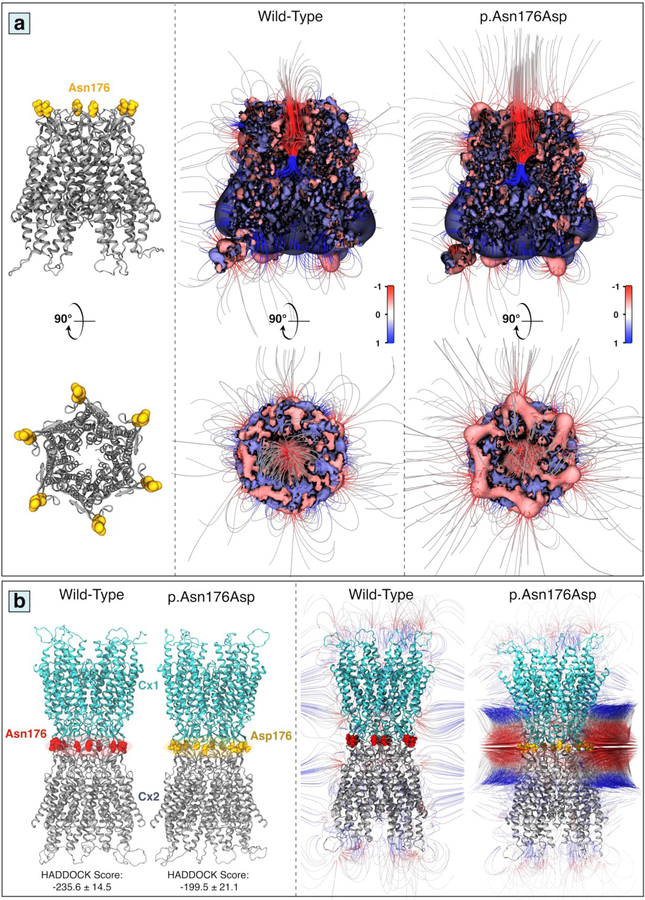
Figure 4.
Molecular architecture of hemichannel and gap junction conformations in wild-type and mutant Cx26. (a) The location of p.Asn176Asp mutation on the top of Cx26 hemichannel is indicated in a ribbon grey representation (left panel). Computed electrostatic potentials and electrostatic fields projected on the surface of the Cx26 in wild-type (middle panel), and p.Asn176Asp (right panel) forms; positive and negative potentials are shown in blue and red, respectively (color scale is 1 to +1 kTe−1). (b) Modeled structure of Cx26 gap junction channels in wild-type (left) and mutant p.Asn176Asp (right) conformations predicted by HADDOCK (left panel); Electrostatic field-lines with positive and negative electrostatic potentials are shown in blue and red, respectively (right panel) (color scale is −1 to +1 kTe−1).