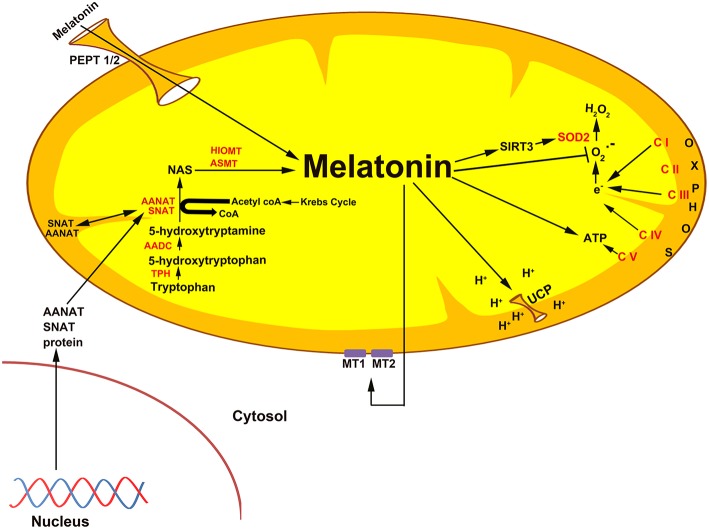
Figure 3.
The association of melatonin with mitochondria is predicted on the basis of the origin of these organelles as specified in the text. Current evidence suggests that melatonin is synthesized in some species in the mitochondrial matrix as illustrated here. Also, exogenously administered melatonin concentrates in the mitochondria (102), i.e., melatonin is a mitochondria-targeted agent. Given that melatonin functions as an antioxidant is particularly important in mitochondria since these organelles are a major site of free radical generation. In addition to directly neutralizing reactive oxygen species, melatonin also stimulates the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD2), an action that involves an elevated level of sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) (39). Melatonin potentially enters mitochondria through the oligopeptide transporters, PEPT1/2 (103). Melatonin also influences mitochondrial membrane potential by influencing uncoupling protein (UCP). Also, melatonin from the matrix may leak out of the mitochondria to interact with the melatonin receptors, MT1 and MT2, to control the release of cytochrome c.