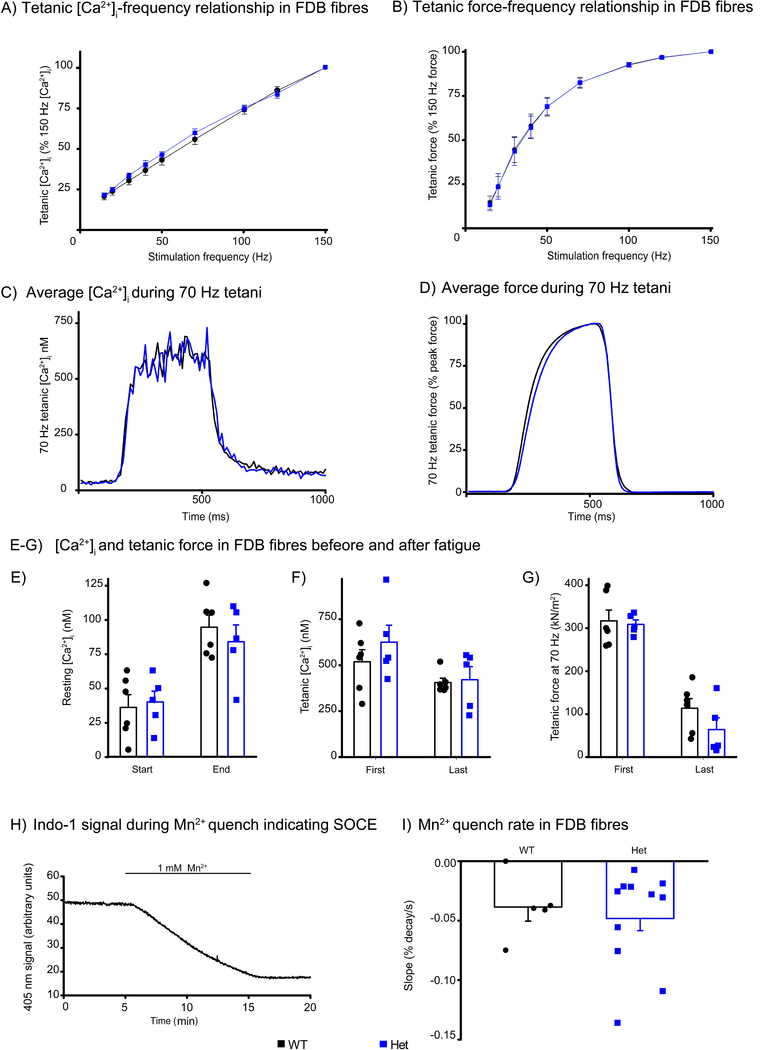
Figure 6. Ca2+ handling in mouse FDB fibres.
(A-B) Tetanic [Ca2+]i-frequency (A) and force-frequency relationships (B) in FDB fibres from wildtype (WT, n=9 fibres) and heterozygous Stim1+/R304W (Het, n=7 fibres) mice showed no difference between the two groups. Tetani were evoked at 1 minute intervals.
(C-D) Comparable averaged tetanic [Ca2+]i records (C) and force records (D) were observed from 70 Hz tetanic contractions in wildtype (WT, n=9) and Stim1+/R304W heterozygous (Het, n=7) FDB fibres from at least three mice in each group.
(E-G) Resting [Ca2+]i (E), tetanic [Ca2+]i (F), and tetanic force (G) were similar in wildtype (n=6) and Stim1+/R304W (n=5) FDB fibres both at the start and end of fatigue induced by 150 repeated tetani. Symbols represent the individual values obtained in fibres.
(H) A typical record of the Indo-1 fluorescent signal at 405 nm during a Mn2+ quenching experiment performed to assess SOCE in a single FDB fibre. Mn2+ present during the experiment indicated.
(I)Mn2+ quenched the Indo-1 signal at the same rate in wildtype (WT, n=5) and heterozygous Stim1+/R304W (Het, n=11) fibres.