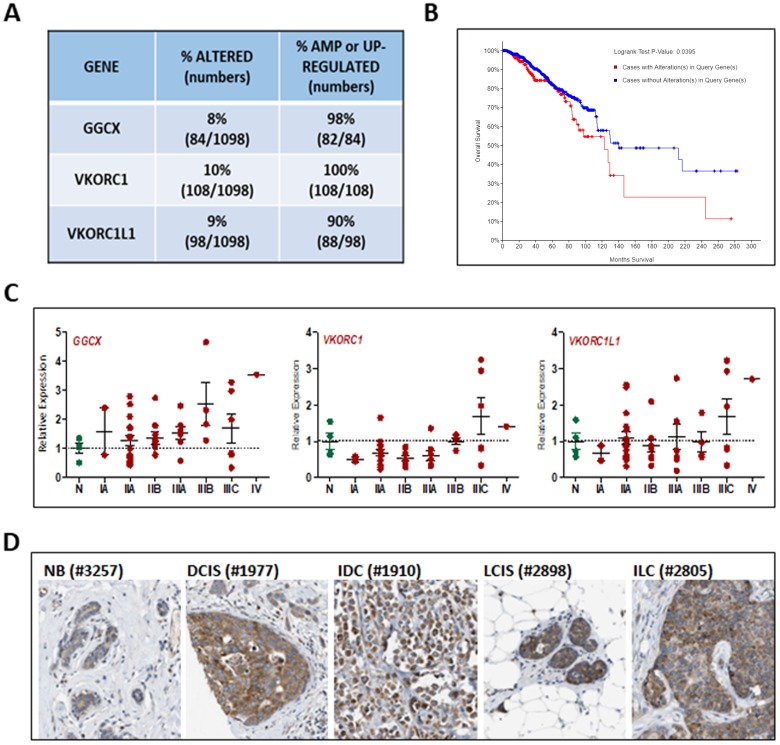
Figure 1. Relevance of vitamin K pathway to human breast cancer.
(A) Analysis of genomic alterations in GGCX, VKORC1, and VKORC1L1 genes obtained from the TCGA dataset of 1098 breast cancers. The following alterations were included: mutations based on exome sequencing, copy number alterations based on the GISTIC (Genomic Identification of Significant Targets in Cancer) algorithm, and mRNA z-scores based on RNA-Seq data (threshold ± 2). (B) Kaplan Meier analysis indicated reduced median survival of patients whose tumors harbor mutations in GGCX, VKORC1, and VKORC1L1. (C) GGCX, VKORC1, and VKORC1L1 expression in human breast tumor tissue samples. TissueScan™ Disease Tissue qPCR Arrays (#BCRT104, Origene) were used to assess gene expression in 48 samples (4-normal, 2-Stage IA, 15-Stage IIA, 9-Stage IIB, 7-Stage IIIA, 4-Stage IIIB, 6-Stage IIIC, 1-Stage IV). Data was normalized to β-Actin expression and expressed relative to values obtained from normal tissue (N). Bars represent mean ± SEM. (D) GGCX protein expression in human breast tumors. Images of tissues immunostained with validated antibody against GGCX (Atlas Antibodies HPA018284) from the Human Protein Atlas [25]. NB-normal breast, DCIS-ductal carcinoma in situ, IDC-invasive ductal carcinoma, LCIS-lobular carcinoma in situ, ILC-invasive lobular carcinoma. Numbers in parentheses refer to deidentified patient codes.