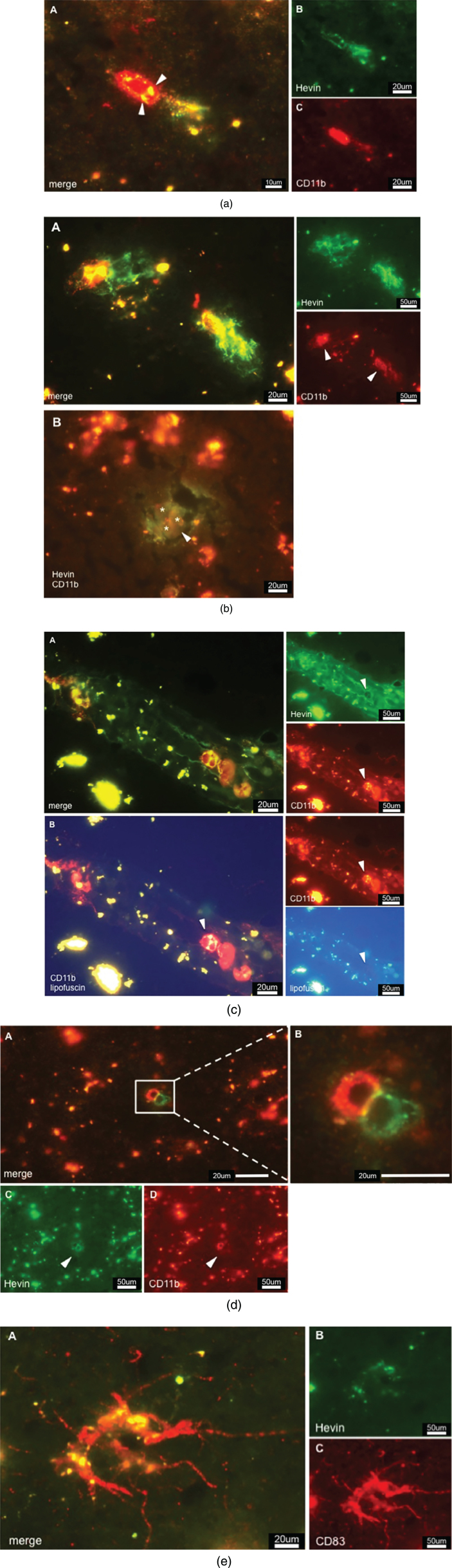
Fig.4.
a) CD11b positive cell expressing Hevin in AD tissue. Colocalization is indicated by color overlay, highlighted here by white arrowheads. Based on the cell-size this cell could be a macrophage. b) Hevin expression in AD tissue. A: Hevin is expressed in areas where lipofuscin is detectable – an indication of active macrophages taking care of dying neurons and neuronal debris. B: But Hevin is also detected around plaques (arrowhead). CD11b positive microglia (asterisks) are located in pathological areas. We suggest that Hevin induces alternative activation of microglia for tissue repair. c) A: Hevin positive structures contain CD11b positive cells that, at the same time, are strongly Hevin positive, indicated by arrowheads. B: Lipofuscin is not associated with Hevin positivity. Arrowheads highlight a Hevin+/CD11b + cell that is free of lipofuscin as the yellow signal disappears upon UV exposure. d) Cells that show different expression of specific cell markers. C demonstrates Hevin immunoreactivity, whereas D is positive for CD11b. B is an enlarged view at the cells from A. The yellow-appearing color suggests a strong interaction of both cells. e) Activated dendritic cell in AD tissue. CD83 immunoreactivity gave proof of the presence of DCs in the brain. Hevin expression as shown in B, however, cannot be correlated to DCs. Hevin positivity in respect to CD83 was neglected although image A appears to show Hevin positivity in the overlay. Overlooking the brain sections, there was hardly any Hevin immunoreactivity.