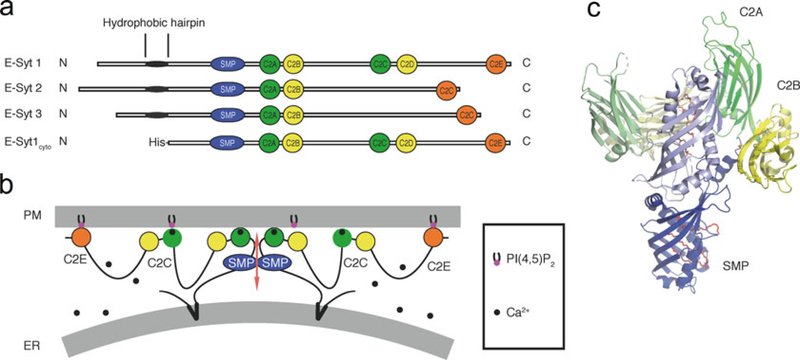
Fig. 1.
Architecture and structure of the E-Syts. (a) Domain organization of the E-Syts and of the E-Syt1 construct used for the membrane tethering and lipid transfer assays. (b) Schematic representation of the putative arrangement of E-Syt1 at ER-PM contacts in the presence of elevated cytosolic Ca2+ (see also [5]). The protein dimerizes via its SMP domain. The C2A and the C2C domains have Ca2+-binding sites. (c) Crystal structure of an E-Syt2 fragment comprising its SMP domain and C2A-C2B domains (PDB code: 4P42). One monomer is shown in full colors and the other in pale colors. The SMP domain is in blue, the C2A domain is in green, and the C2B domain is in yellow. Lipid molecules are represented as sticks in red