Key Figure, Figure 3: Plasma cell isotype defines effector function heterogeneity.
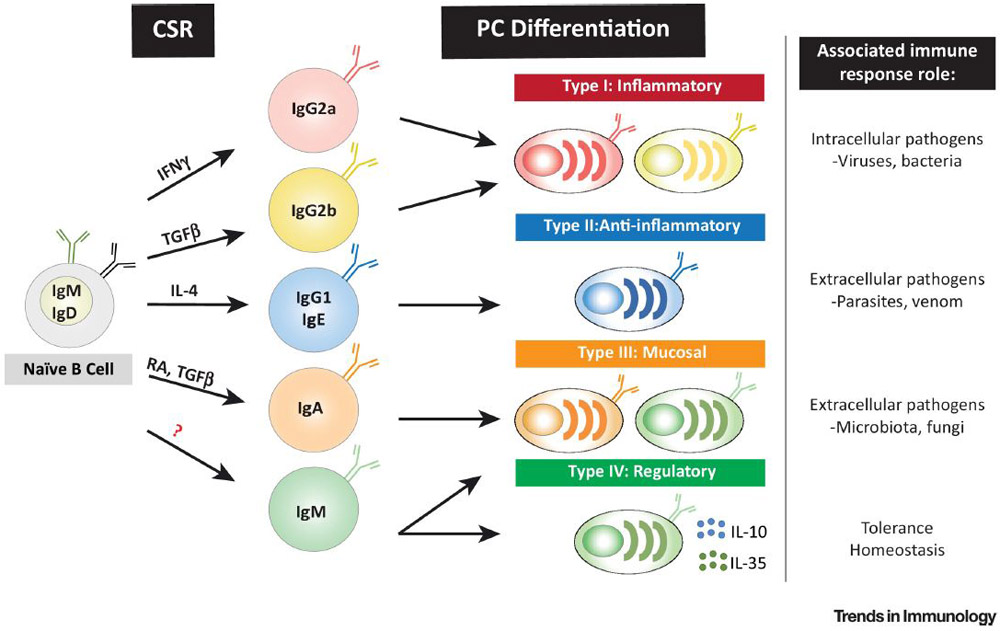
Helper T (TH) cell derived factors specifically elicit class switch recombination (CSR) in B cells to certain isotypes. Both T cell help and CSR likely imprint distinct transcriptional programs that influence B cell lineage fate and function, and which are maintained through terminal differentiation. As emphasized by terminally differentiated plasma cells, B cell isotypes participate in discrete immune responses through secreted cytokines and antibodies. B cell immunity can therefore be assorted into the four major categories of immunity used for TH and innate lymphoid cell subsets: type I inflammatory, type II anti-inflammatory, type III mucosal, and regulatory immunity (herein described as type IV). Abbreviations: IFNγ, Interferon gamma; RA, Retinoic acid; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β
