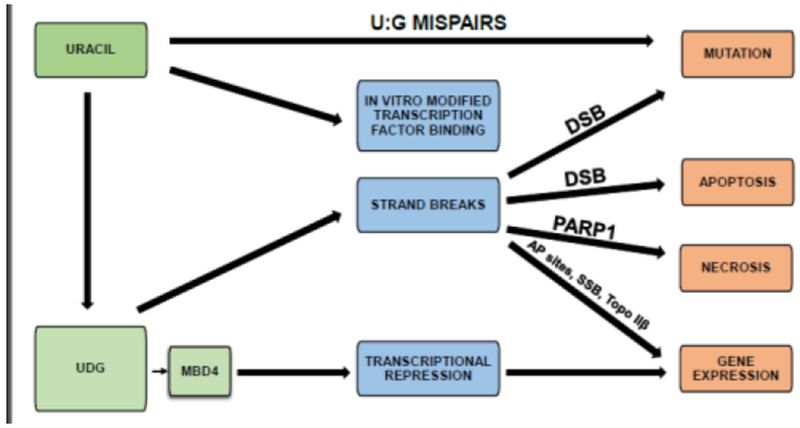
Figure 3. Consequences of uracil in DNA.
Cytosine deamination induces U:G mispairs. In vitro replacement of thymine with uracil modifies transcription factor binding. Repair of uracil induces strand breaks, which can lead to mutation or apoptosis. Potentially, these strand breaks can induce necrosis, and modify gene expression through AP sites, single strand breaks, orTopo IIβ. MBD4 inhibits transcription, modifying gene expression. MBD4, Methyl-CpG binding domain ;protein 4. DSB, double strand breaks; PARP1, Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; AP, abasic sites; SSB, single strand breaks; Topo IIβ, Topoisomerase IIβ.