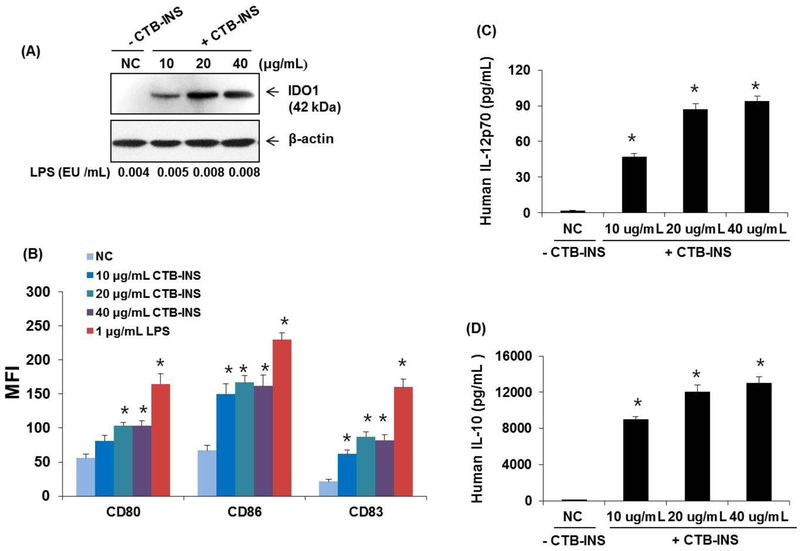
Figure 7. Increased amounts of CTB-INS stimulate DC activation and cytokine secretion.
Panel (A) Immunoblot detection of IDO1 levels in human moDCs treated with increasing amounts of LPS free CTB-INS. PBS treated DCs are a negative control (NC) for addition of CTB-INS. The amount of LPS in each CTB-INS treated DC sample was determined by the Limulus amebocyte lysate assay. Actin protein bands provide a loading control for DC protein in each well. Panel (B) graphic representation of costimulatory factors CD80, CD86 and CD83 synthesized on LPS free CTB-INS treated DCs determined by flow cytometric detection of fluorescent Ab binding to DC co-stimulatory factors (MFI). Panels (C and D) graphic representation of ELISA determination of pro-inflammatory (IL-12p70) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines secreted by DCs into the culture medium following treatment of the DCs with increasing amounts of LPS free CTB-INS. Individual bars represent the mean and standard deviation (SD) of three independent ELISA cytokine determinations. *p < 0.05, in comparison with NC.