FIGURE 5.
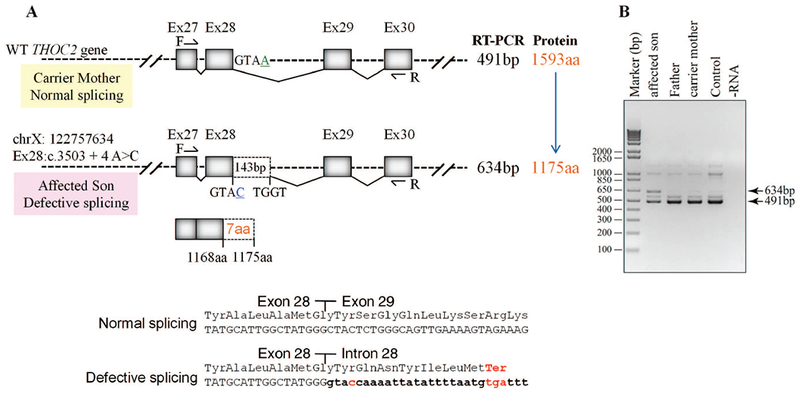
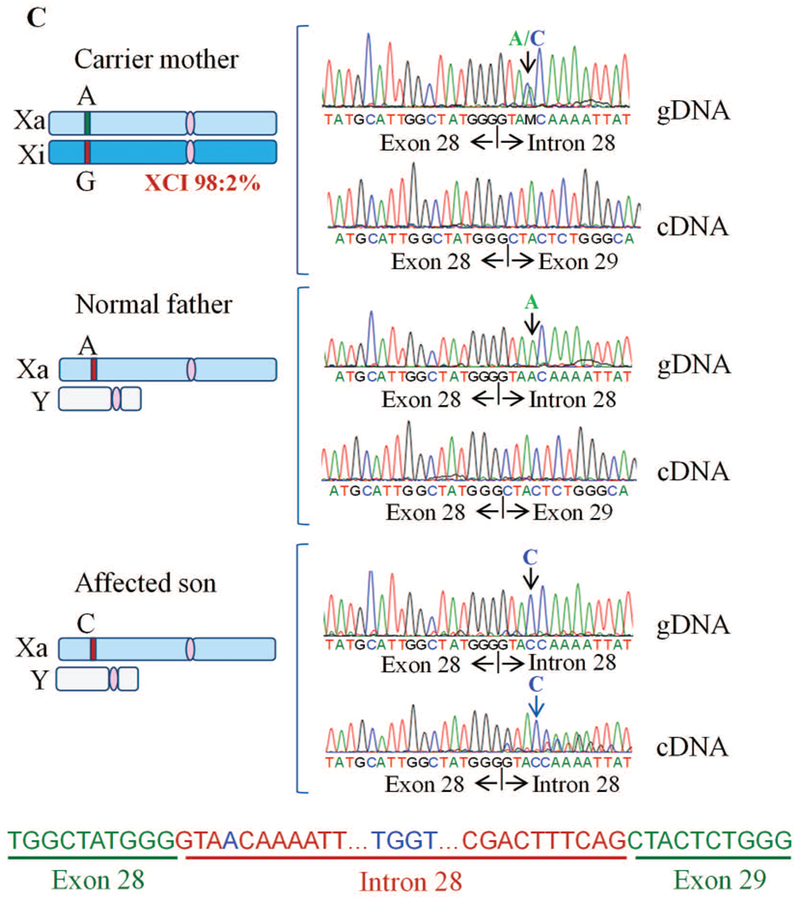
Exon28:c.3503+4A>C variant causes aberrant splicing of intron between exons 28-29 A: Part of the THOC2 gene showing location of the A/C nucleotide in the heterozygous carrier mother and A>C splice variant in the affected son. The C-terminal part of the 1593 amino acid wild type and 1175 amino acid (that contains 1168 normal and 7 amino acids coded by the unspliced intron) THOC2 protein in the affected son are also shown. B: Gel showing a 491 bp RT- PCR product from the normally-spliced heterozygous carrier mother and unaffected father, and 491 bp and 634 bp (retaining 143 bp of the 503 bp intron between exons 28-29) RT-PCR products derived from the normally and aberrantly spliced mRNAs, respectively, in the affected son. Location of the forward and reverse primers within exons 27 and 30 is shown. C: Sanger sequencing chromatograms of PCR products amplified using primers located within exons 27 and 30 from genomic and cDNA of unaffected father and mother and the affected son.
