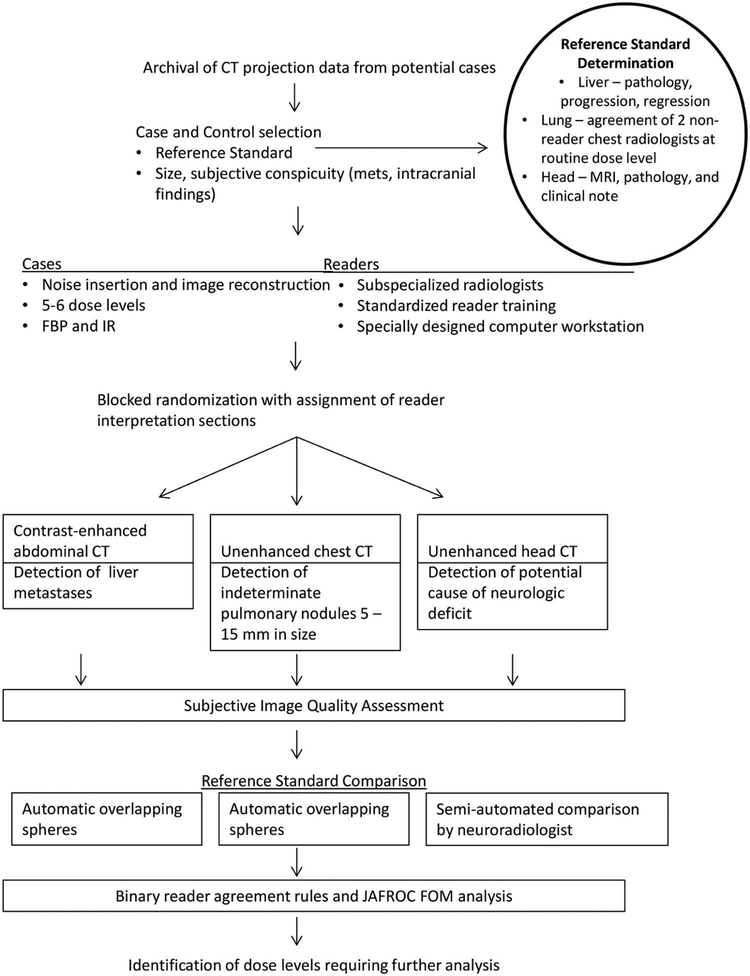
Figure 1.
Study schema. For each of three common diagnostic tasks in CT imaging (contrast-enhanced abdominal CT to detect liver metastases, unenhanced chest CT to detect indeterminate pulmonary nodules, and unenhanced head CT to detect cause of neurologic deficit), three subspecialized radiologists examined CT images corresponding to 5 or 6 dose levels reconstructed with both FBP and IR, using a specially designed computer workstation to mark target lesions of interest, with reader markings and confidence compared to an established reference standard. Reader agreement rules and a JAFROC figure of merit were used to compare observer performance at varying dose levels.