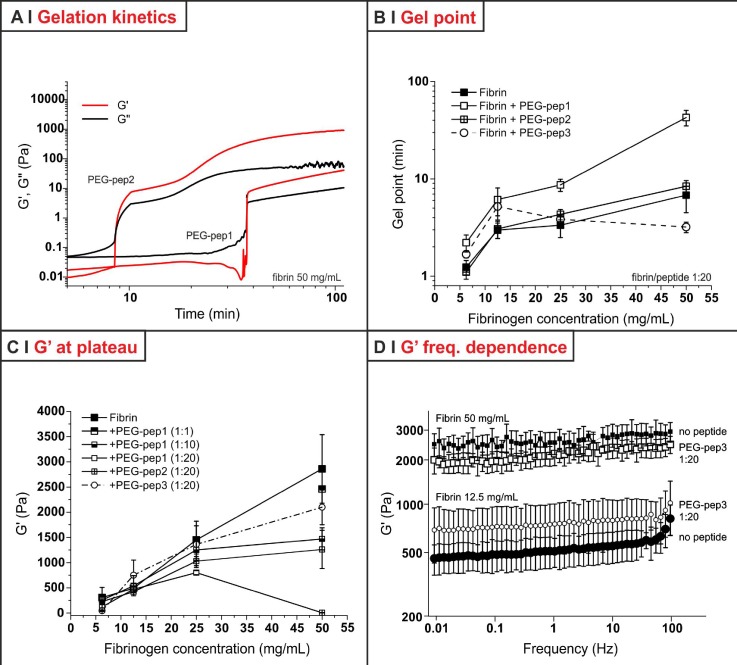
FIG. 2.
(a) Storage (G′) and loss (G″) modulus (stress = 5 Pa, frequency = 1 Hz) as a function of time for two PEG-peptides mixtures with fibrinogen (1:20 molar ratio to fibrinogen 50 mg/ml). (b) Gel point values (time at which G′ = G″; stress = 5 Pa, frequency = 1 Hz) for fibrin gels with and without PEG-peptides (fibrinogen/PEG-peptide molar ratio of 1:20, corresponding to a PEG peptide concentration of 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, and 7.9 mg/ml for fibrinogen 6.25 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/ml, respectively). Note that at a fibrinogen concentration of 6.25 mg/ml, all gel points are statistically indistinguishable. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of independent samples (n = 3). (c) Plateau (time > 100 min) values of storage shear modulus (G′) for fibrin gels with and without PEG-peptides (stress = 5 Pa, frequency = 1 Hz; fibrinogen/PEG-peptide molar ratio in the legend); the effect of the latter not only had no trend (at 12.5 mg/ml PEG-pep3 caused a small increase in the average value of G′, at 50 mg/ml a small decrease), but is also barely significant. (d) Plateau values of G′ as a function of frequency, showing that PEG-pep3 did not introduce any statistically significant effect both at an intermediate (12.5 mg/ml) and a high (50 mg/ml) concentration of fibrin.