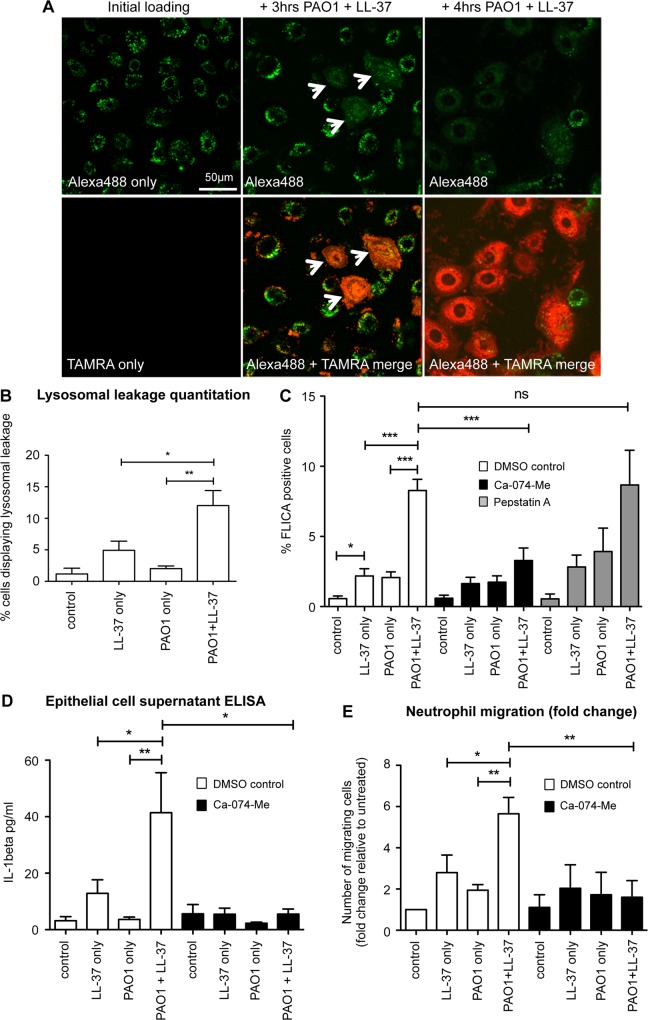
Fig 7. LL-37-induced activation of caspase-1 in P. aeruginosa infected epithelial cells, and induction of neutrophil migration, is mediated by lysosomal leakage of cathepsin B.
A) Confocal microscopy images of NHBE cells loaded with Alexa 488 Dextran (green) +/- treatment with TAMRA-labelled LL-37 (red), with white arrows indicating lysosomal leakage, quantified in (B). ** p<0.01, * p<0.05, data represent mean +/- SEM for n ≥ 3 per condition. C—E) NHBE cells were treated for 3 hours with media only (control), 20 μg/ml LL-37, PAO1 at 10:1 MOI, or PAO1 + LL-37. Some cells were pre-exposed for 1 hour to cathepsin B inhibitor CA-074-Me (20 μM) (C—E), or cathepsin D inhibitor Pepstatin A (20 μM) (C). C) Caspase 1 activation was assessed by FLICA assay D) IL-1β in the supernatant was quantified by ELISA. E) Neutrophil migration in ChemoTx plates towards conditioned supernatant from NHBE cells was assessed. Data represent means +/- SEM from n = 3–6 independent experimental repeats, *** p < 0.001, ** p<0.01, * p < 0.05, by 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-test. ns = no significant difference.