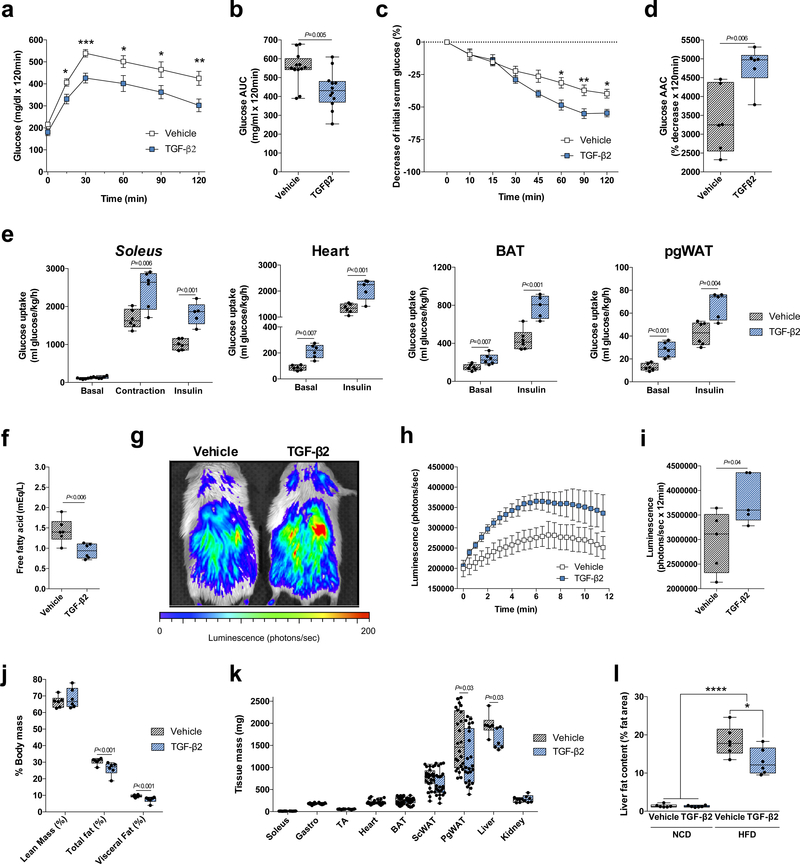
Figure 4.
TGF-β2 infusion via osmotic pump ameliorates the effects of a high fat diet in mice. (a) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) and (b) GTT area under the curve in high fat diet-fed (HFD) mice treated with TGF-β2; n=12 mice. (c) Insulin tolerance test (ITT) and (d) ITT area above the curve; n=6 mice. (e) [3H]-2-deoxyglucose uptake in soleus, heart, BAT, and pgWAT; n=5 or 6 mice. (f) Serum free fatty acid concentrations in HFD mice; n=6 mice. (g) Representative image of luciferin-conjugated fatty acid uptake, (h) quantification of luciferin activity and (i) area under the curve (AUC) in mice. n=5 mice. (j) Lean, total fat and visceral fat mass; n=6 mice. (k) Tissue mass; n=24 mice. (l) Liver fat content in normal chow diet-fed (NCD) or HFD mice; n=8 mice. Data are presented as box plots (min, max, median, and 25th and 75th percentiles) with dots as individual values (b, d, e, f, i, j, k and l), or mean ± s.e.m (a, c, and h). Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for b, d, e, f, i, j and k. ANOVA was used for a, c, and l. When ANOVA showed P<0.05, Tukey’s multiple comparisons tests were used with *P<0.05; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.