Fig. 3. KHK-A acts as a protein kinase and phosphorylates p62 at S28.
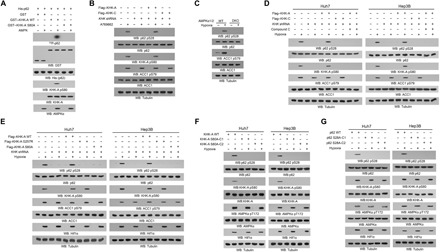
Immunoblot analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. (A) An in vitro AMPK kinase assay was performed by mixing bacterially purified WT GST–KHK-A, GST–KHK-A S80A, or GST on glutathione agarose beads with or without purified active AMPK in the presence of AMP and ATP for 1 hour. The glutathione agarose beads were then washed and incubated with purified His-p62 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Autoradiography was performed. (B) Huh7 cells with or without expressing KHK shRNA and with or without reconstituted expression of the indicated proteins were treated with or without A769662 (0.5 mM) for 4 hours in the presence of the lysosome inhibitor CQ (10 μM). (C) WT and AMPKα1/2 DKO MEFs were treated with or without hypoxia for 6 hours in the presence of the lysosome inhibitor CQ (10 μM). (D) Huh7 and Hep3B cells with or without expressing KHK shRNA and with or without reconstituted expression of the indicated KHK proteins were pretreated with or without compound C (5 μM) for 30 min before hypoxia stimulation for 6 hours in the presence of the lysosome inhibitor CQ (10 μM). (E) Huh7 and Hep3B cells with or without expressing KHK shRNA and with or without reconstituted expression of the indicated proteins were treated with or without hypoxia for 6 hours in the presence of the lysosome inhibitor CQ (10 μM). (F and G) Parental Huh7 and Hep3B cells and the indicated clones of cells with knock-in of KHK-A S80A (F) or p62 S28A (G) expression were stimulated with or without hypoxia for 6 hours in the presence of the lysosome inhibitor CQ (10 μM).
