Fig. 5. SpASFF1 cleaves a P-type S3:19 acylsucrose but not an F-type S3:22 acylsucrose.
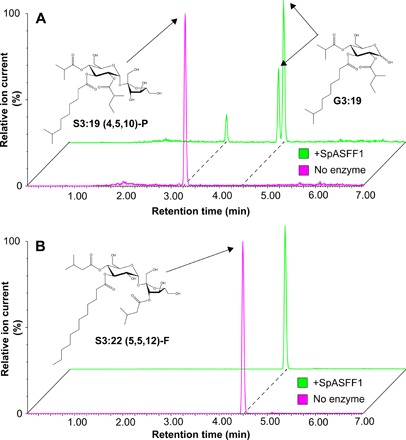
(A) LC-MS analysis of in vitro enzyme assay products indicates that SpASFF1 hydrolyzed P-type S3:19 (4R4,5R2,10R3) acylsucrose, yielding two compounds with m/z 533.3. This m/z is consistent with an acylglucose product with a G3:19 (4,5,10) configuration; the two peaks represent the α and β anomers of the acylglucose. (B) LC-MS analysis of in vitro assays with F-type S3:22 (5R4,5R3′,12R3) acylsucrose indicates no hydrolysis products with SpASFF1. Acylglucose structure is inferred from collision-induced dissociation-mediated fragmentation (fig. S9). All ESI− mode acylsugars were identified as formate adducts.
