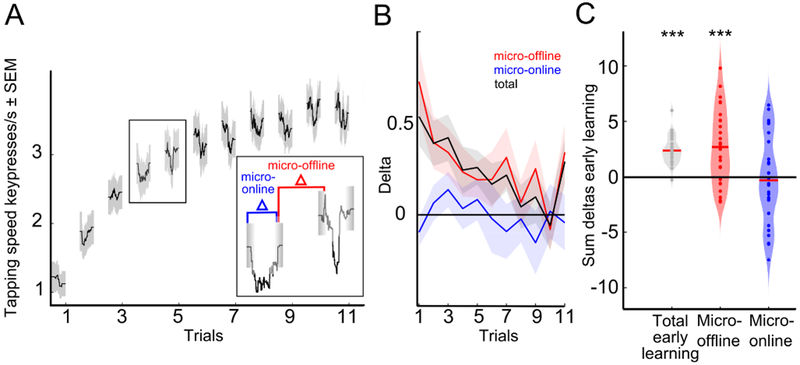
Figure 2. Early online learning was evidenced during short rest periods.
A, Microscale early learning reveals performance increments over rest periods. Micro-online changes were calculated as the difference in tapping speed (keypresses/s) of the first and last correct sequence within a practice period (blue in inset) and micro-offline changes as the difference between the last correct sequence within a practice period compared to the first of the next practice period (red in inset). B, Trial-wise early learning. Each line depicts performance changes (micro-offline in red, micro-online in blue, total in black) per trial (mean + s.e.m.). Total learning is closely accounted for by micro-offline gains (black and red lines) whereas micro-online performance changes fluctuate around 0. Note the presence of large micro-offline gains and total early learning in the initial trials in the absence of micro-online performance decrements. Subsequently, within-practice performance decrements manifested gradually as learning slowed down. C, Data points in the violin plot depict the sum of changes in performance over early learning trials in each participant. Note that total early learning is accounted for by performance improvements during rest periods, but not during practice periods (two-tailed one-sample t test for each learning partition, ***P < 0.001, FDR-corrected for multiple comparisons). See also Figure S1.