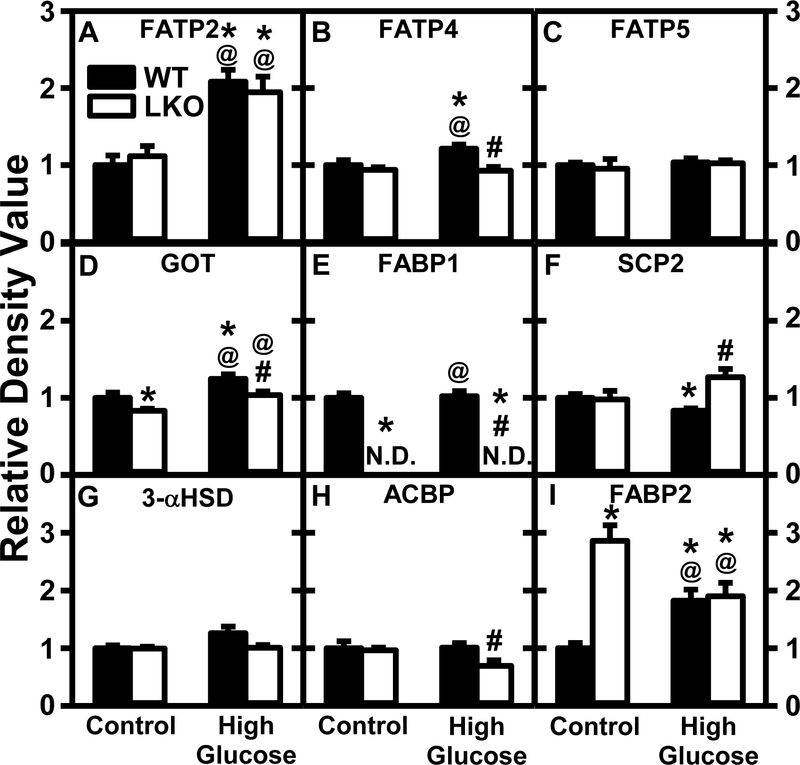
Figure 10. Pair-fed high glucose diet (HGD) has greater effect than Lfabp gene ablation (LKO) on protein levels of key liver fatty acid transporters.
All conditions were as in legend of Fig. 9 except that SDS-PAGE and Western blotting were performed to determine relative hepatic protein levels of: Group 1: membrane fatty acid transport proteins, i.e. FATP2 (Fig. 10A; Supplemental Fig. 7B), FATP4 (Fig. 10B; Supplemental Fig. 11A), and FATP5 (Fig. 10C; Supplemental Fig. 11B) and GOT (Fig. 10D; Supplemental Fig. 12A); Group 2: cytosolic fatty acid/fatty acyl CoA binding proteins, i.e. FABP1 (Fig. 10E; Supplemental Fig. 4A, 9B, 12A), SCP2 (Fig. 10F; Supplemental Fig. 6B, 8B,13A), 3-αHSD (Fig. 10G; Supplemental Fig. 10A), ACBP (Fig. 10H; Supplemental Fig. 8A, 11B), and FABP2 (Fig. 10I; Supplemental Fig. 10B). Western blot images for each protein (n=7) along with GAPDH, COX4, or β-actin housekeeper for normalization are shown in the respective Supplemental Figs. 4–17. WT (Black bars) and LKO (Open bars). Values represent the mean ± SEM, n=7, with statistical significance indicated as follows: * p≤ 0.05 vs WT mice on control diet; @ p≤ 0.05 vs LKO mice on control diet; and #p≤ 0.05 vs WT mice HGD.