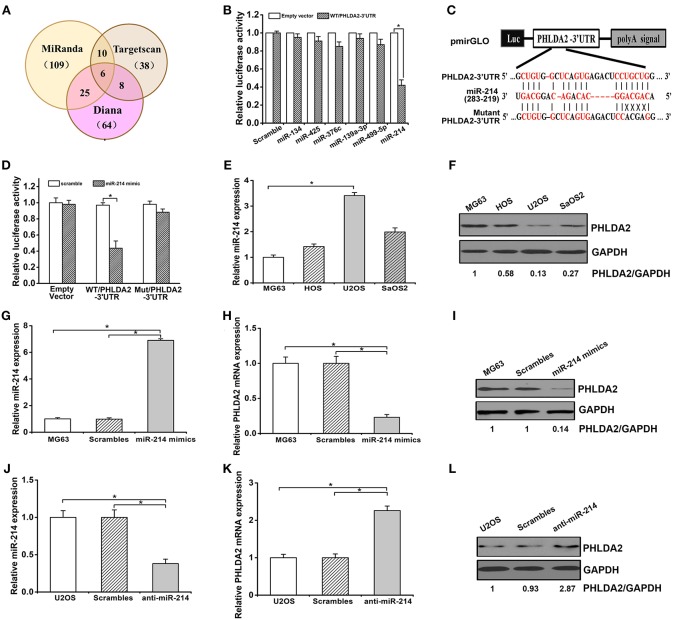
Figure 1.
miR-214 targets PHLDA2. (A) Bioinformatics analysis of candidate miRNAs with potential binding sites in PHLDA2 3′UTR. Digits in brackets represented the total number of miRNAs predicted by each database. (B) Luciferase assay showed miR-214 mimics inhibited reporter activity with wild-type PHLDA2-3′UTR in HEK293T cells. (C) Schematic illustration of a pmirGLO luciferase vectors with PHLDA2 3′-UTR and sequence alignment of PHLDA2-3′UTR (top) with hsa-miR-214 (middle). Bottom, substitution of four bases (UGCU to ACGA) at the binding sites of miR-214 to construct the mutate vector (Matant PHLDA2 3′UTR). (D) The inhibition of reporter activity was abolished by mutant vector with PHLDA2-3′UTR. (E,F) qRT-PCR and western blot for miR-214 expression and PHLDA2 protein in four osteosarcoma cell lines, respectively. (G) qRT-PCR for miR-214 expression in MG63 cells without and with scrambles or miR-214 mimics. (H,I) miR-214 mimics decreased the mRNA and protein level of PHLDA2 in MG-63 cells, respectively. (J) qRT-PCR for miR-214 expression in U2OS cells without and with scrambles or anti-miR-214. (K,L) Anti-miR-214 upregulated the mRNA and protein level of PHLDA2 in U2OS cells, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05.