Figure 3.
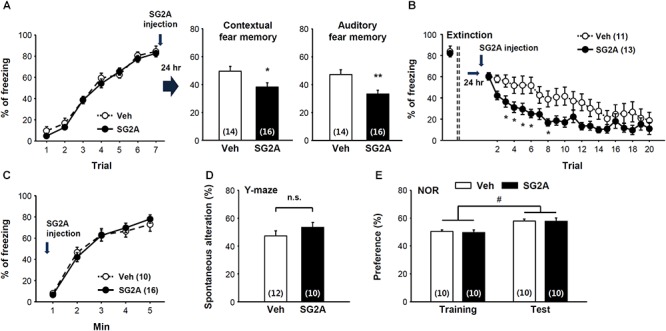
Effect of SG2A on fear memory consolidation and extinction. (A) Decreased fear memory consolidation by SG2A. Fear memory acquisition curves during seven repeated tones and foot shock pairing (left). SG2A was administered immediately after acquisition, and contextual fear memory (middle) and auditory fear memory (right) were determined 24 h later. (B) Facilitated extinction of consolidated fear memory by SG2A. 24 h after memory acquisition, freezing behaviors were scored during 20 trials of a 30-s tone without foot shock in the distinct context in the presence or absence of SG2A. (C) Innate fear response is unaltered by SG2A. Freezing behaviors of mice exposed to TMT were scored. (D) Recognition memory by SG2A in the Y maze. No significant difference (n.s.) was found between Veh- and SG2A-treated groups. (E) Novel object recognition test. Vehicle- and SG2A-treated mice similarly showed a preference for the novel object. Data are presented as means ± SEMs; ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. Veh, #P < 0.05 between training and test group. Numbers in parentheses indicated the numbers of animals used for each group.
