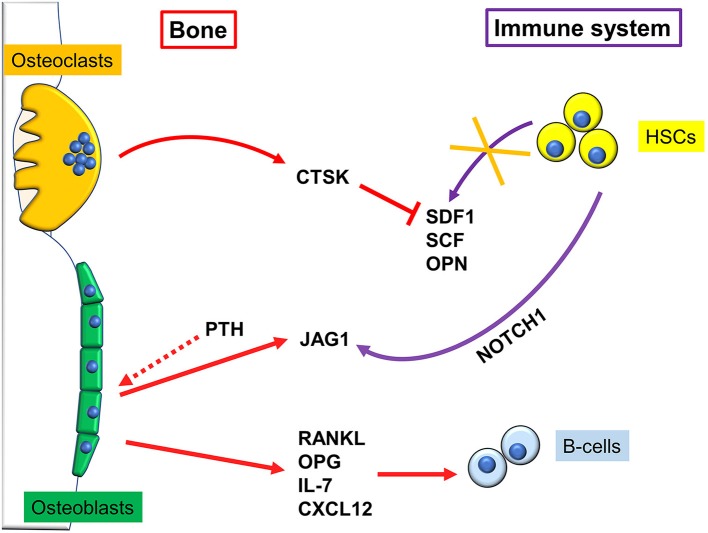
Figure 2.
Regulation of immune cells by bone cells. Osteoclasts reduce hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) homing by secreting cathepsin K (CTSK), which in turn degrades stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)1, stem cell factor (SCF), and osteopontin (OPN) depriving the bone niche of HSC-binding sites, which causes their mobilization. Osteoblasts, after stimulation with pro-osteoblastogenic factors such as intermittent parathyroid hormone (PTH), express Jagged1 (Jag1), which binds NOTCH1 on HSCs, and allows them to engraft and survive into the endosteal niche. B cells and bone cells communicate in multiple ways. For example, osteoblasts produce IL-7 and the chemokine CXCL12, that are fundamental for B-cells survival and activity.