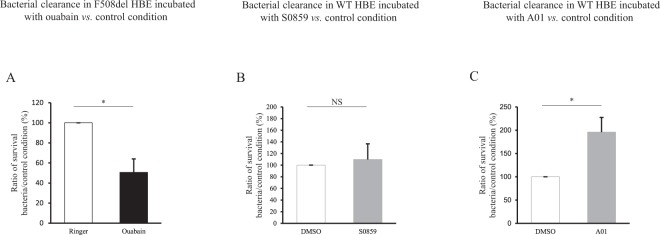
Figure 7.
Effect of pH pharmacological modulation on clearance of S. aureus CIP 76.25 in airway surface liquid of WT and F508del Human Bronchial Epithelial primary cells. Human Bronchial Epithelial (HBE) primary cells were apically infected with S. aureus CIP 76.25 (3,000 CFU/ml) for 2 hours previously incubated with specific transporter inhibitors or vehicle. The apical fluid was collected at the end of the experiments and plated on Petri dishes to count surviving bacteria. Bacteria detected under test conditions were expressed as ratio to the control condition. (A) F508del HBE cells incubated with ouabain 1 mM, as ATP12A inhibitor vs. Ringer for 2 hours. % of surviving bacteria from inoculum: 50.6 ± 13%, p = 0.046. For all conditions, n = 2 in triplicate. (B) WT HBE cells incubated with S0859 100 µM, as NBC inhibitor, vs. DMSO for 2 hours. % of surviving bacteria from inoculum: 109.7 ± 27%, NS. For all conditions, n = 2 in triplicate. (C) WT HBE cells incubated with A01 25 µM, as SLC26A4 inhibitor, vs. DMSO for 6 hours. % of surviving bacteria from inoculum: 196 ± 32%, p = 0.028. For all conditions, n = 2 in triplicate. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance from unpaired nonparametric Wilcoxon test. *p < 0.05; NS: non significant.