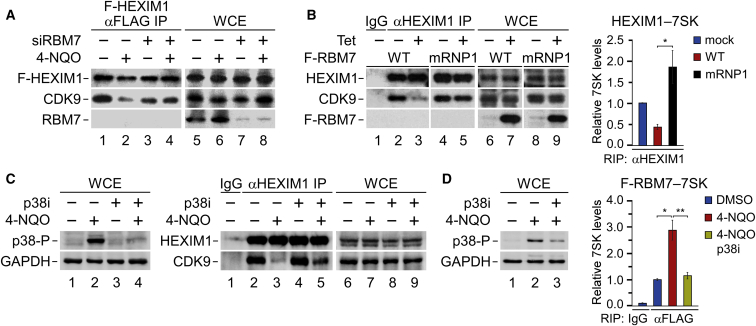
Figure 3.
RBM7 Is Critical for the Genotoxic-Stress-Induced Release of P-TEFb from HEXIM1
(A) CoIP of F-HEXIM1 with CDK9 and RBM7 from WCE of HEK293 cells. Conditions with control (−) and RBM7 siRNA #1 (+) and with (+) and without (−) 4-NQO are shown.
(B) Left: CoIP of HEXIM1 with CDK9 from WCEs of HEK293 cells containing wild-type and mRNP1 F-RBM7. Conditions with (+) and without (−) F-RBM7 induction by tetracycline (Tet) are shown. Right: RIP-qPCR of 7SK in HEXIM1 IP from WCE of HEK293 cells containing wild-type and mRNP1 F-RBM7. Conditions with wild-type (red bars), mRNP1 (black bars), and without (blue bars) F-RBM7 induction by Tet are shown. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05, determined by Student’s t test.
(C) CoIP of HEXIM1 with CDK9 from WCEs of HeLa cells. Conditions with (+) and without (−) 4-NQO or p38i are shown. Levels of phospho-p38MAPK (p38-P) indicate activation of p38MAPK.
(D) RIP-qPCR of 7SK in F-RBM7 IP from WCEs of HeLa cells. Conditions with 4-NQO (red bars), 4-NQO and p38i (yellow bars), and without 4-NQO (blue bars) are shown. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, determined by Student’s t test. Levels of phospho-p38MAPK (p38-P) indicate activation of p38MAPK.