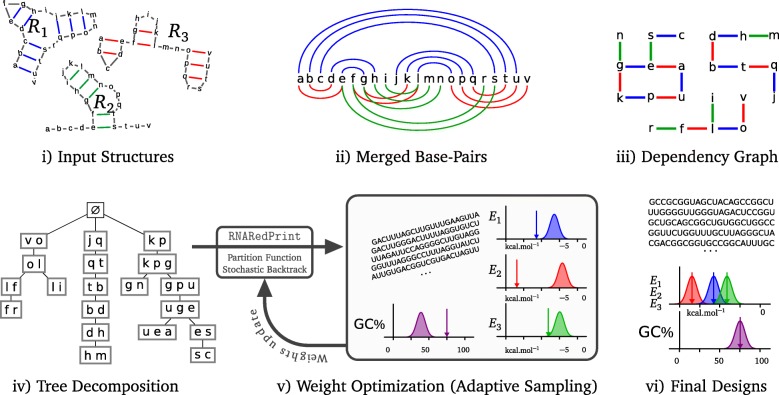
Fig. 1.
General outline of  . From a set of target secondary structures (i), base pairs are merged (ii) into a (base pair) dependency graph (iii) and transformed into a tree decomposition (iv). The tree is then used to compute the partition function, followed by a Boltzmann sampling of valid sequences (v). An adaptive scheme learns weights to achieve targeted energies and GC% (arrows), leading to the production of suitable designs (vi). Note that for simplicity, we assume in this figure that only dependencies between the ends of base pairs are considered to evaluate the energies of structures. Our computations based on a more complex energy model, which considers energy contributions of base pair stacks, require additional dependencies
. From a set of target secondary structures (i), base pairs are merged (ii) into a (base pair) dependency graph (iii) and transformed into a tree decomposition (iv). The tree is then used to compute the partition function, followed by a Boltzmann sampling of valid sequences (v). An adaptive scheme learns weights to achieve targeted energies and GC% (arrows), leading to the production of suitable designs (vi). Note that for simplicity, we assume in this figure that only dependencies between the ends of base pairs are considered to evaluate the energies of structures. Our computations based on a more complex energy model, which considers energy contributions of base pair stacks, require additional dependencies