Fig. 1.
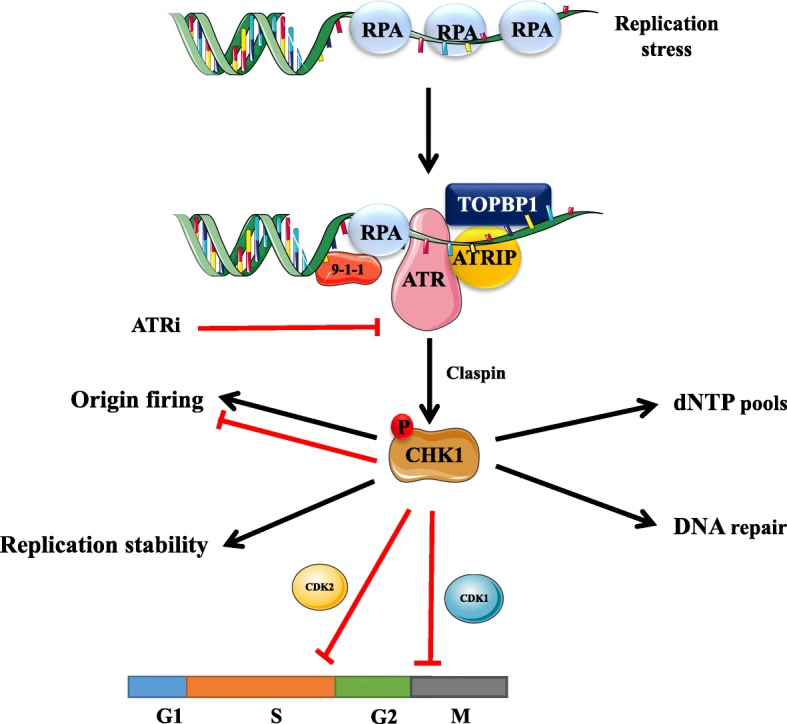
Replication stress induced ATR-CHK1 activation. ATR is activated by replication protein A (RPA)-coated single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) that arises at stalled replication fork or resected DNA double-strand break (DSB), particularly at ssDNA and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) juncture. The recruitment of ATR-interacting protein (ATRIP) leads to recognition of ATR and RPA-ssDNA complex. Subsequently, it incorporates Rad9-Rad1-hus1 (9-1-1) and DNA topoisomerase 2-binding protein 1 (TOPBP1), leading to ATR activation. Mediated by adaptor protein claspin, ATR phosphorylates checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1). The activation of CHK1 can prevent genomic instability. The mechanisms are either promoting or inhibiting the initiation of DNA replication (origin firing), ensuring sufficient supply of deoxynucleotides (dNTPs) pool, stabilizing replication fork and DNA repair. Its downstream molecules, cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 1 and CDK2, suppresses G2-M transition and slows down S phase
