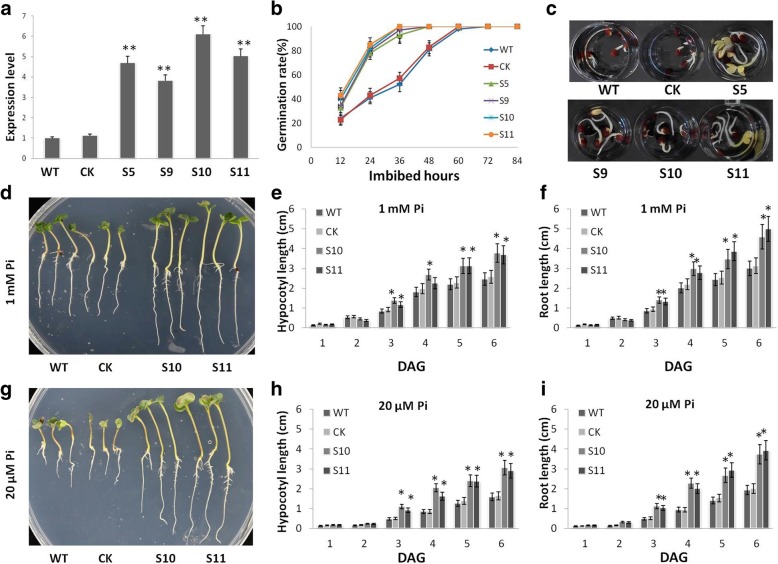
Fig. 3.
BnPHT1;4 promotes seed germination and seedling growth of Brassica napus. (a) Detection of the transcript abundance of BnPHT1;4 in the BnPHT1;4 overexpression transgenic seedlings and controls (WT and CK) by quantitative RT-PCR analysis. Total RNA was isolated from roots and shoots of the 7 DAG seedlings. Expression levels of the BnPHT1;4 in wild type are set to 1, and in the transgenic lines are shown in folds compared with that in wild type. The error bars indicate the standard errors. Significance of difference was analyzed by Duncan’s test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, n = 3). (b and c) Overexpression of BnPHT1;4 promotes seed germination. Seed germination of the BnPHT1;4 overexpression transgenic lines and controls on 1/2 MS medium with 1000 μM Pi. Seeds were stored for 2 months after harvest and subjected to analysis. After seeds were sowed, quantitative analysis of germination rates at different time (hours of seed imbibition) are shown in b, and one representative image per genotype (1.5 days after sowing) is shown in c. (d-i) Overexpression of BnPHT1;4 promotes early seedling growth. Seeds of the controls were sowed about 24 h earlier than those of BnPHT1;4 transgenic lines, and then the seedlings with same length of radicle grew on 1/2 MS medium with 20 or 1000 μM Pi. KCl was used to replace KH2PO4 in the medium for the equivalent amount of potassium. One representative image per genotype (1.5 days after sowing) is shown in d (1000 μM Pi) and g (20 μM Pi). Quantitative analysis of hypocotyl length and root length in 1000 μM Pi are shown in e and f, while in 20 μM Pi are shown in h and i. Five experimental replications were performed and each replication contains at least l50 seedlings. The data are presented as means ± SD (n = 5). WT, wild type; CK, transgenic null line; S5, S9, S10 and S11, four independent BnPHT1;4 overexpression transgenic lines. DAG, day after germination