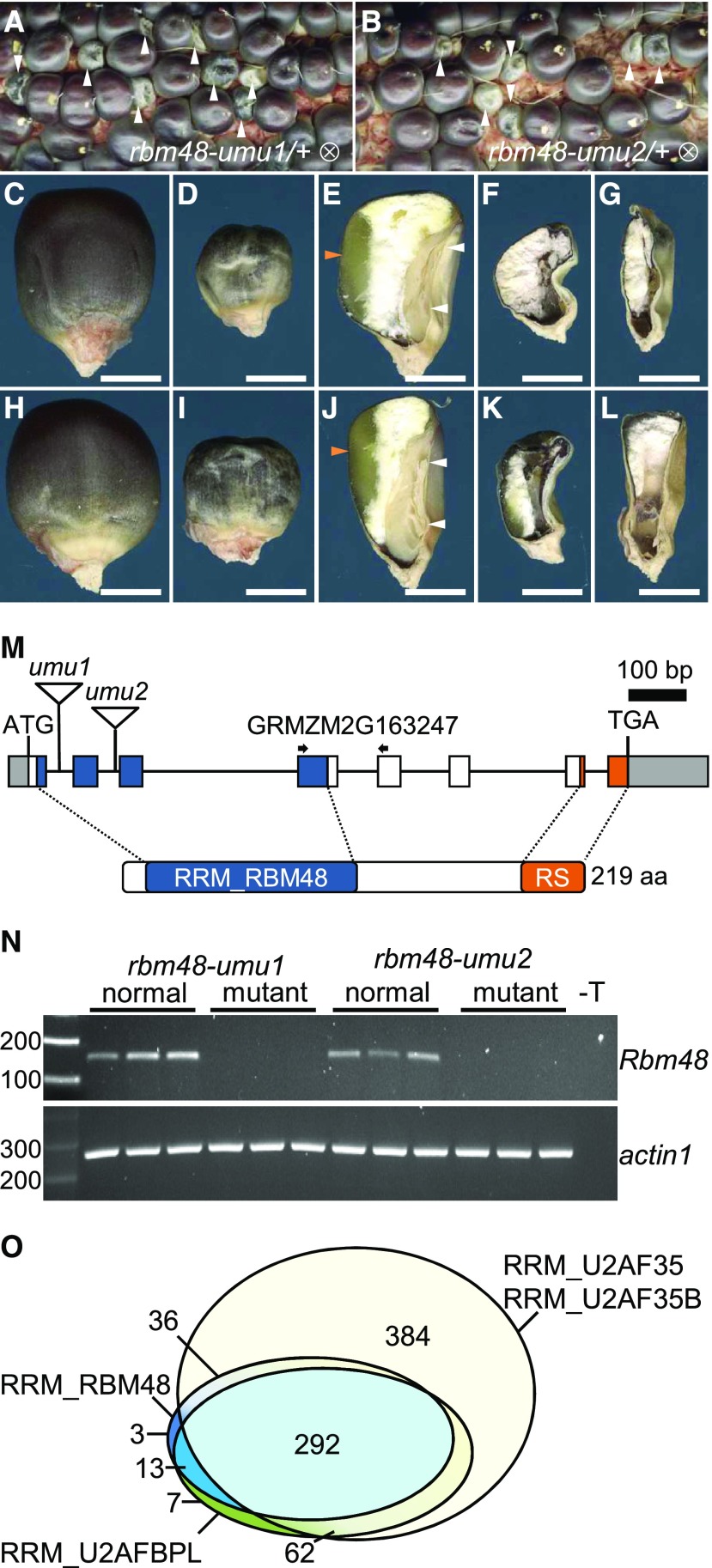
Figure 1.
Mutant Alleles of rbm48.
(A) and (B) Segregating self-pollinated ears for rbm48-umu1 and rbm48-umu2 alleles. Arrowheads indicate rbm48 mutant kernels.
(C) to (L) Mature kernel phenotypes for rbm48-umu1 (C) to (G) and rbm48-umu2 (H) to (L). Abgerminal view of normal siblings (C) and (H), rbm48-umu1 (D), and rbm48-umu2 (I). Sagittal sections of normal siblings (E) and (J), rbm48-umu1 (F) and (G), and rbm48-umu2 (K) and (L). Scale bars = 0.5 cm. White arrowheads indicate shoot and root of the embryo. Orange arrowheads indicate vitreous endosperm.
(M) Schematic of the Rbm48 locus, GRMZM2G163247, and protein domain structure. Triangles indicate transposon insertions causing rbm48-umu1 and rbm48-umu2. Arrows indicate primers for RT-PCR in panel (N).
(N) RT-PCR analysis of Rbm48 and actin1 control in rbm48-umu1 and rbm48-umu2, and their normal siblings. T is a no template DNA negative control.
(O) Proportional Venn diagram showing the number of species in the NCBI Conserved Domain Database with RRM domains from RGH3 (RRM_U2AFBPL), RBM48 (RRM_RBM48), and U2AF1 (RRM_U2AF35 union with RRM_U2AF35B).