Fig. 13.
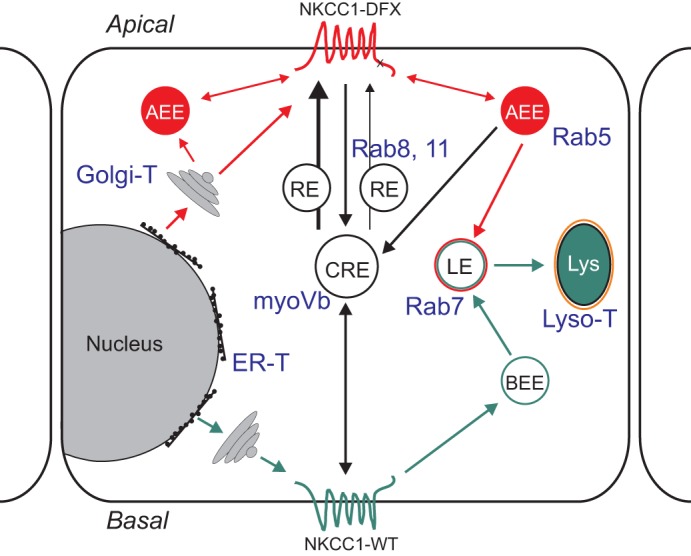
Model depicting the trafficking of NKCC1 wild-type and mutant in polarized epithelial cell. Wild-type NKCC1 (green pathway) is targeted to the basolateral membrane following its exit from the Golgi. The basolateral NKCC1-WT could be endocytosed and trafficked to the basolateral early endosome (BEE) where they can either be recycled to the membrane or targeted to late endosomes and lysosomes for degradation. NKCC1 COOH terminal mutants are trafficked to the apical membrane (red pathway). From the apical membrane these mutants could be endocytosed in apical early endosomes (AEE) and then trafficked to common recycling endosome (CRE), late endosomes and lysosomes. Some proteins could be recycled to the apical membrane from the CRE, or AEE. In blue font: compartment-specific antibodies and dyes used in this study.
