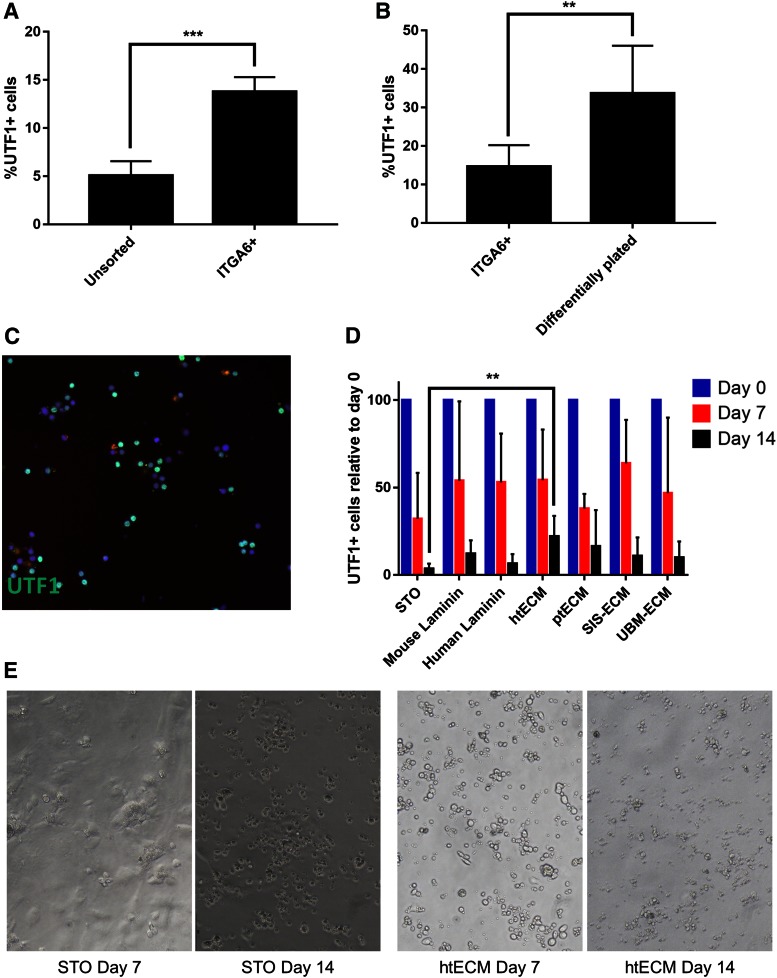
FIG. 4.
Enrichment and culture of undifferentiated spermatogonia on ECM substrates. (A) MACS was used to enrich UTF1+ undifferentiated spermatogonia from human testicular cell suspensions based on the expression of ITGA6. Immunocytochemical analysis was then performed to show that UTF1+ cells were enriched in the positive fraction compared with unsorted cells (p = 0.0042). (B) To further enrich UTF1+ cells and contaminating somatic cells, MACS-sorted ITGA6+ cells were differentially plated on collagen I. Selected cells had a higher number of UTF1+ cells compared with ITGA6+ fraction of the sort (p = 0.0153). (C) Illustrative picture of immunostaining for UTF1 expression used to quantify enrichment of cells in (A, B) and maintenance of cells in culture. (D) Immunocytochemical analysis of UTF1 expression was performed on cells at the time of initiation of culture (day 0) and at days 7 and 14 of culture. UTF1+ cells were significantly depleted in all culture conditions by day 14 (p = 0.0001); however, htECM retained a significantly higher number of UTF1+ cells day 14 compared with the control STO feeder cell condition (p = 0.039). (E) Illustrative bright-field microscopy images of human spermatogonia cultured on STO feeder cells and htECM at days 7 and 14. Bar graphs are represented as mean ± SEM. **p<0.005, ***p<0.0005. ITGA6, integrin alpha-6; MACS, magnetic-activated cell sorting; SEM, standard error of the mean; SIM, Sandos inbred mice; STO, SIM 6-thioguanine-resistance, ouabain-resistant; UTF1, undifferentiated embryonic cell transcription factor 1; UTF1+, undifferentiated embryonic cell transcription factor 1-positive. Color images are available online.